Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Acceleo/Acceleo Operations Reference
Contents
- 1 Acceleo operationq reference
- 1.1 Standard String Operations
- 1.1.1 first (Integer n) : String
- 1.1.2 index (String r) : Integer
- 1.1.3 isAlpha () : Boolean
- 1.1.4 isAlphanum () : Boolean
- 1.1.5 last (Integer n) : String
- 1.1.6 strcmp (String s1) : Integer
- 1.1.7 strstr (String r) : Boolean
- 1.1.8 strtok (String r, Integer n) : String
- 1.1.9 substitute (String r, String t ) : String
- 1.1.10 toLowerFirst () : String
- 1.1.11 toUpperFirst () : String
- 1.2 Standard Integer operations
- 1.3 Standard Real operations
- 1.1 Standard String Operations
- 2 Acceleo non standard operations reference
- 2.1 Non-standard *String* operations
- 2.1.1 contains (String substring) : Boolean
- 2.1.2 endsWith (String substring) : Boolean
- 2.1.3 equalsIgnoreCase (String other) : Boolean
- 2.1.4 lastIndex (String r) : Integer
- 2.1.5 matches (String regex) : Boolean
- 2.1.6 replace (String substring, String replacement) : String
- 2.1.7 replaceAll (String substring, String replacement) : String
- 2.1.8 startsWith (String substring) : Boolean
- 2.1.9 substituteAll (String substring, String replacement) : String
- 2.1.10 substring (Integer startIndex) : String
- 2.1.11 tokenize (String substring) : Sequence(String)
- 2.1.12 trim () : String
- 2.2 Non-standard *EObject* operations
- 2.2.1 ancestors () : Sequence(EObject)
- 2.2.2 ancestors (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
- 2.2.3 eAllContents () : Sequence(EObject)
- 2.2.4 eAllContents (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
- 2.2.5 eContainer (OclType oclType) : oclType
- 2.2.6 eContents (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
- 2.2.7 eGet (String featureName) : EJavaObject
- 2.2.8 eInverse () : Sequence(EObject)
- 2.2.9 eInverse (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
- 2.2.10 followingSiblings () : Sequence(EObject)
- 2.2.11 followingSiblings (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
- 2.2.12 precedingSiblings () : Sequence(EObject)
- 2.2.13 precedingSiblings (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
- 2.2.14 siblings () : Sequence(EObject)
- 2.2.15 siblings (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
- 2.3 Non-standard *OclAny* operations
- 2.3.1 current (Integer index) : OclAny
- 2.3.2 current (OclType filter) : OclAny
- 2.3.3 getProperty (String key) : OclAny
- 2.3.4 getProperty (String key, Sequence(OclAny) parameters) : OclAny
- 2.3.5 getProperty (String name, String key) : OclAny
- 2.3.6 getProperty (String name, String key, Sequence(OclAny) parameters) : OclAny
- 2.3.7 invoke (String class, String method, Sequence(OclAny) arguments ) : OclAny
- 2.3.8 toString () : String
- 2.4 Non-standard *Collection* operations
- 2.1 Non-standard *String* operations
Acceleo operationq reference
Standard String Operations
first (Integer n) : String
Returns the first *n* characters of *self*, or *self* if its size is less than *n*.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'first operation'.first(8) | 'first op' |
| 'first operation'.first(-1) | invalid |
index (String r) : Integer
Returns the index of substring *r* in *self*, or -1 if *self* contains no occurrence of *r*.
- Important:* String indexes start at 1. Consequently the last character's index in a string is equal to the string's length.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'index operation'.index('op') | 7 |
| 'index operation'.index('i') | 1 |
| 'index operation'.index('foo') | -1 |
isAlpha () : Boolean
Returns *true* if *self* consists only of alphabetical characters, *false* otherwise.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'isAlpha'.isAlpha() | true |
| 'isAlpha operation'.isAlpha() | false (spaces are not alphabetical characters) |
| 'isAlpha11'.isAlpha() | false (digits are not alphabetical characters) |
isAlphanum () : Boolean
Returns *true* if *self* consists only of alphanumeric characters, *false* otherwise.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'isAlphanum'.isAlphanum() | true |
| 'isAlphanum operation'.isAlphanum() | false |
| 'isAlphanum11'.isAlphanum() | true |
last (Integer n) : String
Returns the last *n* characters of *self*, or *self* if its size is less than *n*.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'first operation'.last(8) | 'peration' |
| 'first operation'.last(40) | 'first operation' |
| 'first operation'.last(-1) | invalid |
strcmp (String s1) : Integer
Returns an integer that is either negative, zero or positive depending on whether *s1* is alphabetically less than, equal to or greater than *self*. Note that upper case letters come before lower case ones, so that 'AA' is closer to 'AC' than it is to 'Ab'.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'strcmp operation'.strcmp('strcmp') | 10 |
| 'strcmp operation'.strcmp('strcmp operation') | 0 |
| 'strcmp operation'.strcmp('strtok') | -17 |
strstr (String r) : Boolean
Searches for string *r* in *self*. Returns *true* if found, *false* otherwise.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'strstr operation'.strstr('ope') | true |
| 'strstr operation'.strstr('false') | false |
strtok (String r, Integer n) : String
Breaks *self* into a sequence of tokens, each of which delimited by any one of the characters in *s1*, and return the next element in this sequence. The parameter flag should be *0* when strtok is called for the first time and will reset the sequence, *1* subsequently so as to access the next element.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'strtok operation'.strtok('opz', 0) | 'strt' |
| 'strtok operation'.strtok('pn', 0) | 'strtok o' |
substitute (String r, String t ) : String
Substitutes substring *r* in *self* by substring *t* and returns the resulting string. Will return *self* if it contains no occurrence of the substring *r*.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'substitute operation'.substitute('t', 'T') | 'subsTiTuTe operaTion' |
| 'foobar foobar foobar'.substitute('t', 'T') | 'foobar foobar foobar' |
toLowerFirst () : String
Creates a copy of *self* with its first character converted to lower case and returns it.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'ToLowerFirst operation'.toLowerFirst() | 'toLowerFirst operation' |
toUpperFirst () : String
Creates a copy of *self* with its first character converted to upper case and returns it.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'toUpperFirst operation'.toUpperFirst() | 'ToUpperFirst operation' |
Standard Integer operations
toString () : String
Converts the integer *self* to a string.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 2009.toString() | '2009' |
Standard Real operations
toString () : String
Converts the real *self* to a string.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| (-5.3).toString() | '-5.3' |
Acceleo non standard operations reference
Non-standard *String* operations
contains (String substring) : Boolean
Returns *true* if *self* contains the substring *substring*, *false* otherwise.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'contains operation'.contains('ins op') | true |
| 'contains operation'.contains('2009') | false |
endsWith (String substring) : Boolean
Returns *true* if *self* ends with the substring *substring*, *false* otherwise.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'endsWith operation'.endsWith('ation') | true |
| 'endsWith operation'.endsWith('endsWith') | false |
| 'anything'.endsWith() | true |
equalsIgnoreCase (String other) : Boolean
Returns *true* if *self* is equal to the string *other* ignoring case considerations, otherwise returns *false*. Two strings are considered equal ignoring case if they are of the same length and corresponding characters in the two strings are equal ignoring case.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'lowercase'.equalsIgnoreCase('LOWERCASE') | true |
| 'lowercase'.equalsIgnoreCase('lowercase') | true |
| 'lowercase'.equalsIgnoreCase('lowerCase') | true |
| 'lowercase'.equalsIgnoreCase('uppercase') | false |
lastIndex (String r) : Integer
Returns the last index of substring *r* in *self*, or -1 if *self* contains no occurrence of *r*. *Important:* String indexes start at 1. Consequently the last character's index in a string is equal to the string's length.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'index operation'.lastIndex('op') | 7 |
| 'index operation'.lastIndex('o') | 14 |
matches (String regex) : Boolean
Returns *true* if *self* matches the given regular expression pattern *regex*, *false* otherwise. The regex engine used is that of your runtime JDK. The given pattern is passed "as is" to the method *matches* of the java class *String*. For more about regular expressions, please refer to the JDK API documentation.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'characters and spaces'.matches('[\\w\\s]+') | true |
| 'characters and 3 digits'.matches('[\\w\\s]+') | false |
replace (String substring, String replacement) : String
Substitutes the first occurrence of substring *substring* in *self* by substring *replacement* and returns the resulting string. Returns *self* if it contains no occurrence of *substring*. Note that both *substring* and *replacement* are treated as regular expressions.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'replace operation'.replace('p', 'P') | 'rePlace operation' |
| 'repla ce operation'.replace('(\\\\w+)\\\\s*', '\\\\1') | 'replace operation' |
replaceAll (String substring, String replacement) : String
Substitutes all substrings *substring* in *self* by substring *replacement* and returns the resulting string. Returns *self* if it contains no occurrence of *substring*. Note that both *substring* and *replacement* are treated as regular expressions.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'replaceAll operation'.replaceAll('p', 'P') | 'rePlaceAll oPeration' |
| 'Repla ce All Operation'.replaceAll('(\\\\w+)\\\\s*', '\\\\1') | 'ReplaceAllOperation' |
startsWith (String substring) : Boolean
Returns *true* if *self* starts with the substring *substring*, *false* otherwise.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'startsWith operation'.startsWith('star') | true |
| 'startsWith operation'.startsWith('ope') | false |
| 'anything'.startsWith() | true |
substituteAll (String substring, String replacement) : String
Substitutes all substrings *substring* in self by substring *replacement* and returns the resulting string. Returns *self* if it contains no occurrence of *substring*. Unlike the *replaceAll* operation, neither *substring* nor *replacement* are considered as regular expressions.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'substituteAll operation'.substituteAll('t', 'T') | 'subsTiTuTeAll operaTion' |
substring (Integer startIndex) : String
Returns a substring of *self*, starting at *startIndex* (inclusive), until the end of *self*. Returns |invalid| when the *startIndex* is either negative, zero, or greater than *self*'s length. *Important:* String indexes start at 1. Consequently the last character's index in a string is equal to the string's length.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'short term'.substring(7) | 'term' |
| 'short term'.substring(-1) | invalid |
| 'short term'.substring(0) | invalid |
| 'short term'.substring(10) | 'm' |
| 'short term'.substring(11) | invalid |
tokenize (String substring) : Sequence(String)
Returns a sequence containing all parts of self split around delimiters defined by the characters in String delim.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| 'tokenize operation'.tokenize('e') | Sequence{'tok', 'niz', ' op', 'ration'} |
| 'tokenize operation'.tokenize('i') | Sequence{'token', 'ze operat', 'on'} |
trim () : String
Removes all leading and trailing white space characters (tabulation, space, line feed, ...) of *self*.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| ' trim operation '.trim() | 'trim operation' |
Non-standard *EObject* operations
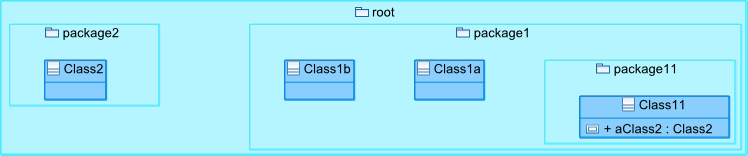
All of the examples from this section are set in the context of this model (with **root** being an instance of *Model* as per the UML metamodel) :
ancestors () : Sequence(EObject)
Returns a Sequence containing the full set of the receiver's ancestors.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class11.ancestors() | Sequence{package11, package1, root} |
| package11.ancestors() | Sequence{package1, root} |
ancestors (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
Returns the elements of the given type from the set of the receiver's ancestors as a Sequence. The returned sequence's elements are typed with the expected type (so there's no need to invoke @oclAsType(oclType)@ on the sequence or its elements).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class11.ancestors(Package) | Sequence{package11, package1} |
| package11.ancestors(Package) | Sequence{package1} |
eAllContents () : Sequence(EObject)
Returns the whole content tree of the receiver as a Sequence.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| root.eAllContents() | Sequence{package1, package11, Class11, Class1a, Class1b, package2, Class2, aClas2} |
| package1.eAllContents() | Sequence{package11, Class11, Class1a, Class1b} |
eAllContents (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
Returns the elements of the given type from the whole content tree of the receiver as a Sequence. The returned sequence's elements are typed with the expected type (so there's no need to invoke @oclAsType(oclType)@ on the sequence or its elements).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| root.eAllContents(Class) | Sequence{Class11, Class1a, Class1b, Class2} |
| package1.eAllContents(Class) | Sequence{Class11, Class1a, Class1b} |
eContainer (OclType oclType) : oclType
Returns the first ancestor of the given type, i.e. the first ancestor for which @oclIsKindOf(oclType)@ evaluates to **true**. The returned element is typed with the expected type (so there's no need to invoke @oclAsType(oclType)@ on it). *Important:* users of Acceleo 2.x should note that, contrary to what took place in acceleo 2.x, this operation **never** returns *self* even when @self.oclIsKindOf(oclType)@ is true.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class11.eContainer(Package) | package11 |
| package11.eContainer(Package) | package1 |
| aClass2.eContainer(Package) | package11 |
eContents (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
Returns a sequence of the direct children of *self* that are of the given type, i.e. the direct children for which @oclIsKindOf(oclType)@ evaluates to **true**. The returned sequence's elements are typed with the expected type (so there's no need to invoke @oclAsType(oclType)@ on the sequence or its elements).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| package1.eContents(Class) | Sequence{Class1b, Class 1a} |
eGet (String featureName) : EJavaObject
This will fetch the value of the feature named *featureName* on the current Object. Return type can as well be a collection as a single value.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| package1.eGet('packagedElement') | Sequence{Class1b, Class1a, package11} |
| package1.eGet('name') | 'package1' |
eInverse () : Sequence(EObject)
Returns the set of all objects referencing *self*.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class2.eInverse() | Sequence{package11,aClass2} |
| package11.eInverse() | Sequence{package1} |
eInverse (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
Returns the elements of the given type from the set of the inverse references of *self*. The returned sequence's elements are typed with the expected type (so there's no need to invoke @oclAsType(oclType)@ on the sequence or its elements).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class2.eInverse(Property) | Sequence{aClass2} |
| Class2.eInverse(Package) | Sequence{} |
followingSiblings () : Sequence(EObject)
Returns a Sequence containing the full set of the receiver's following siblings.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class11.followingSiblings() | Sequence{} |
| Class1b.followingSiblings() | Sequence{Class1a, package11} |
followingSiblings (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
Returns the elements of the given type from the set of the receiver's following siblings as a Sequence. The returned sequence's elements are typed with the expected type (so there's no need to invoke @oclAsType(oclType)@ on the sequence or its elements).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class1b.followingSiblings(Package) | Sequence{package11} |
| Class1b.followingSiblings(Class) | Sequence{Class1a} |
| Class1a.followingSiblings(Class) | Sequence{} |
precedingSiblings () : Sequence(EObject)
Returns a Sequence containing the full set of the receiver's preceding siblings.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| package11.precedingSiblings() | Sequence{Class1b, Class1a} |
| Class11.precedingSiblings() | Sequence{} |
| Class1a.precedingSiblings() | Sequence{Class1b} |
precedingSiblings (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
Returns the elements of the given type from the set of the receiver's preceding siblings as a Sequence. The returned sequence's elements are typed with the expected type (so there's no need to invoke @oclAsType(oclType)@ on the sequence or its elements).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| package11.precedingSiblings() | Sequence{Class1b, Class1a} |
| Class1a.precedingSiblings(Package) | Sequence{} |
| Class1a.precedingSiblings(Class) | Sequence{Class1b} |
siblings () : Sequence(EObject)
Returns a Sequence containing the full set of the receiver's siblings.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class11.siblings() | Sequence{} |
| Class1a.siblings() | Sequence{package11, Class1b} |
siblings (OclType oclType) : Sequence(oclType)
Returns the elements of the given type from the set of the receiver's siblings as a Sequence. The returned sequence's elements are typed with the expected type (so there's no need to invoke @oclAsType(oclType)@ on the sequence or its elements).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class11.siblings(Class) | Sequence{} |
| Class1a.siblings(Class) | Sequence{Class1b} |
Non-standard *OclAny* operations
- A note on properties*: properties can be accessed only if they've been added through the API. For this purpose, a number of facilities is provided. You can either override the generated launcher's *addProperties* method and add new paths to properties files there, call manually one of the methods **AcceleoService#addPropertiesFile()** or manually add key/value pairs through **AcceleoService#addProperties()**. Take note that the key/value pairs manually added will *always* take precedence over the properties taken from *.properties* files; and the *first* added property file will always take precedence over subsequently added files.
The example on all four *getProperty* variants will take into account the following setup: we provided the environment with a properties file *a.properties* containing the key/value pair:
a.b.c = This is a parameterized property: {0}
Then we provided it with a file *b.properties* containing the pairs:
a.b.c.d = This is a standard property
a.b.c = Parameterized property with a name conflict: {0}
current (Integer index) : OclAny
Returns the value of the context *index* ranks above the current context. The following example is explained line by line in the "result" column.
[for (p: Package | root.packagedElement)] Iterates over all packages of the Model root
[for (c: Class | p.packagedElement)] Iterates over all classes of the current package
[current(0)/] Allows access to the current class (equivalent to c)
[current(1)/] Allows access to the current package (equivalent to p)
[current(2)/] Allows access to self as it was before the first for loop
[/for]
[/for]
current (OclType filter) : OclAny
This will have the same effect as current(Integer) except that is will return the first context (*self* variable) of the given type, at or above the current one. The following example is explained line by line in the "result" column.
[for (p: Package | root.packagedElement)] Iterates over all packages of the Model root
[for (c: Class | p.packagedElement)] Iterates over all classes of the current package
[current(Class)/] Allows access to the current class (equivalent to c)
[current(Package)/] Allows access to the current package (equivalent to p)
[current(Model)/] Allows access to the the root Model
[/for]
[/for]
getProperty (String key) : OclAny
Returns the value of the property corresponding to the given *key*. Note that parameterized properties will be returned "as is" by this operation (parameters are not processed).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| getProperty('a.b.c') | 'This is a parameterized property: {0}' |
| getProperty('a.b.c.d') | 'This is a standard property' |
| getProperty('a.b.c.d.e') | null |
getProperty (String key, Sequence(OclAny) parameters) : OclAny
Returns the value of the property corresponding to the given key, with its parameters substituted with the given values if any.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| getProperty('a.b.c', Sequence{'substitution'}) | 'This is a parameterized property: substitution' |
| getProperty('a.b.c', Sequence{}) | 'This is a parameterized property: {0}' |
| getProperty('a.b.c.d', Sequence{'substitution'}) | 'This is a standard property' |
getProperty (String name, String key) : OclAny
Returns the value of the property corresponding to the given *key* from a properties file corresponding to the given *name*. Note that parameterized properties will be returned as is with this.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| getProperty('b.properties', 'a.b.c') | 'Parameterized property with a name conflict: {0}' |
| getProperty('a.properties', 'a.b.c.d') | invalid |
getProperty (String name, String key, Sequence(OclAny) parameters) : OclAny
Returns the value of the property corresponding to the given *key* from a properties file corresponding to the given *name*, with its parameters substituted with the given values if any.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| getProperty('b.properties', 'a.b.c', Sequence{'substitution'}) | 'Parameterized property with a name conflict: substitution' |
| getProperty('b.properties', 'a.b.c', Sequence{}) | 'Parameterized property with a name conflict: {0}' |
| getProperty('a.properties', 'a.b.c.d', Sequence{'substitution'}) | invalid |
invoke (String class, String method, Sequence(OclAny) arguments ) : OclAny
Invokes the Java method *method* of class *class* with the given arguments. This will return OclInvalid if the method cannot be called in any way (bad arguments, mispelled name, mispelled signature, encapsulation errors, ...). This is only intended to be used to call Java methods for now.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| invoke('java.lang.String', 'toUpperCase()', Sequence{root.name}) | ROOT |
toString () : String
Returns the String representation of the receiver. Examples depend on the "toString()" implementation of *self*. Let's assume it has been changed to return the object's name:
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| Class11.toString() | 'Class11' |
Non-standard *Collection* operations
sep (String separator) : Sequence(OclAny)
Returns all elements from the source collection separated by an element composed of the String *separator*.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| package1.eContents().name.sep('2009') | Sequence{'Package11', '2009', 'Class1a', '2009', 'Class1b'} |
| package1.eContents().sep('2009') | Sequence{Package11, '2009', Class1a, '2009', Class1b} |
filter (OclType type) : Sequence(OclType)
Filters out of the collection all elements that are not instances of the given type or any of its subtypes. The returned collection is typed according to *type*. Makes it easier to write @select(e | e.oclIsKindOf(type)).oclAsType(type)@.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| package1.eContents().filter(Class) | Sequence{Class1b, Class1a} |
reverse () (Only on ordered collections)
Reverses the order of the collection: the last element becomes the first and vice-versa. Only available on **ordered collections** (Sequence and OrderedSet).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| OrderedSet {1, 2, 3} | OrderedSet {3, 2, 1} |
| Sequence {1, 2, 3} | Sequence {3, 2, 1} |
lastIndexOf (T elt) : Integer (Only on ordered collections)
Returns the position of the given element in the collection it is applied to. Only available on **ordered collections** (Sequence and OrderedSet).
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| OrderedSet {1, 2, 1}->lastIndexOf(1) | 3 |
| Sequence {1, 2, 3}->lastIndexOf(4) | -1 |
| Sequence {1, null}->lastIndexOf(null) | 2 |
| Sequence {1, 2, 3}->lastIndexOf(null) | -1 |
| Acceleo Portal | |
| Project | Project · Installation |
| Features | Acceleo Features · Runtime · Acceleo editor · Views & Perspective · Interpreter · Maven |
| User documentation | Getting Started · User Guide · Acceleo operations reference · OCL operations reference · Text Production Rules · Migration From Acceleo 2.x · Best Practices · Videos · FAQ |
| Developer documentation | Source code · How to contribute · Compatibility · MOFM2T specification · OCL specification |
| Community | Professional Support · Report a bug |