Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Apogy/UserGuide
Table Of Contents
Contents
- 1 Table Of Contents
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Overview
- 4 Quick Start
- 5 The User Interface
Introduction
Apogy was originally developed at the Canadian Space Agency to control space exploration rovers and their associated sensors. Integrating all these systems developed by many different contractors and allowing them to be controlled as an integrated entity represented a challenge. In order works, a tool to plan, validate, execute and monitor integrated operations to support multiple missions was required. The technical team soon realized that a reusable framework could save a lot of work and allow for future growth. Apogy is the result of this thinking.
Apogy was built to:
- Be an organizationally neutral core framework (we did not want to be locked in with any particular contractor proprietary tool);
- Maximizes reuse between missions (keep the work to the specifics of each mission);
In order to so, Apogy:
- Is a component-based architecture that allows systems (ex: instruments, rovers, satellites) to “plug-in” and allow the system developer to concentrate on their system specific needs and the tooling to use them.
- Makes use of Open Source librairies that are Eclipse Public License compatible;
Overview
In Apogy, users control Systems by invoking commands (through Programs) and monitor the System's health through telemetry (i.e. states).
These Systems are operated in a Environment which defines such things as Digital Elevation Maps, orbit models, sun position, etc (i.e. what the Environment contains).

|
User, System, Environment and Data Product. |
The System's command produces result (i.e. returned value, such as an Image, an error code, etc.) that Apogy geo-locates and time tags. This allows the results to be displayed within the 3D Environment. This helps in maintaining the situational awareness of the operator and keep the data in context.
Installing Apogy
TODO
Launching Apogy
TODO
Quick Start
To get you started quickly, we will import an existing Session (one of the example) and then used it to command the Integrated Rover example.
Importing an Existing Session
- Launch Apogy.
- Open the Welcome perspective if not already opened:
- In the top menu bar, select Open New Perspective. This will open the Add Perspective pop-up.
- In the pop-up, select the Projects perspective;
- Press OK.
- In the Welcome perspective, select the Projects view;
- In the Registry list, select org.eclipse.apogy.example.rover.apogy;
- Press Import . This will bring up the New Apogy Project wizard;
- Change the name of the project to MyFirstProject, then press Finish.
- In the Workspace list, select the project you just created, then press Open.
- Verify that the Workspace list displays your project as <Active> MyFirstProject
You now have you first Apogy Session loaded ! This session contains a Integrated Rover System, a Surface Worksite (the Mars Emulation Terrain at the Canadian Space Agency) and a few Programs.
Instantiating the Variables
Before we start our system, we will open the Programs perspective to get ready for invoking commands.
- Open the Programs perspective if not already opened:
- In the top menu bar, select Open New Perspective. This will open the Add Perspective pop-up.
- In the pop-up, select the Programs perspective;
- Press OK.
The Programs perspective provides the view required to created, edit, delete and invoque Programs. At this point, we will bring up the 3D Viewer to show what is in the environment:
- In the top menu bar, select Window→Show View. This will open the Add View pop-up.
- In the pop-up, select the Apogy Views→3D Viewer view;
- Press OK.
The 3D Viewer should show the terrain, the sky, and possibly the Sun, the Moon and the stars (depending on the time-of-day). We are ready to instantiate our system:
- On the status bar, confirm that the Context shows Simulated.
- Press Start. The Start button should become disabled, and the Stop button enabled.
The rover Variable has now been instanciated. In the 3D Viewer, you should see the rover standing on the corner of the terrain. We are almost ready to roll!
Invoking Existing Commands
We are now ready to invoke commands on the rover. For now, we will used the commands (or Operation Call in Apogy parlance) :
- In the Programs perspective, select the Programs view;
- In the Programs list, select A.B;
- Select the Program view: it should be display a list of Operation Call.
- In the Operation Call, select Start, then press Invoke. This will start the rover.
- Ensure you have the 3D Viewer showing the rover and the terrain.
- In the Operation Call, select Move Forward, then press Invoke. The rover should start moving forward.
- In the Operation Call, select Stop Motion, then press Invoke. The rover should stop moving.
You may have noticed that flags displaying a date have been popping-up in the 3D Viewer as Operation Call were being invoked. These flags mark the location of the System when the Operation Call returned and show the time at which the Operation Call execution completed.
Preventing the rover from moving through the terrain
You may have noticed that the rover wheels where driving through the terrain, and not on top of it. This is due to the very simple simulation that is updating the rover position based on its speed (the rover only moves on the XY plane and changes its azimuth). This is of course, not very realistic.
Apogy provides a PoseCorrector concept that can be used to maintain a System wheels (or feet in the case of the example Lander) in contact with the ground. Lets enable the pose corrector. For this, we will use the Vehicle Pose view:
- In the top menu bar, select Window→Show View. This will open the Add View pop-up.
- In the pop-up, select the Vehicle Pose view;
- Press OK.
- In the Vehicle Pose view, press Select.... This will bring up the Variable Feature Reference wizard.
- In the wizard, under Variable, select rover, then under Sub-Type, select mobilePlateform;
- Press OK
- In the Vehicle Pose, select the Pose Corrector tab;
- Check enabled
- Invoke the Operation Call used before : The rover wheels should now follow the terrain !
Creating New Commands
Up to now we have been invoking Operation Call that were already defined in a program. Lets now create our own Operation Call:
- In the Programs perspective, select the Programs view;
- Select the TODO Program Group, then press New Program. This will bring up the New Program Wizard:
- On the left side, select OperationCallsList (this is a Program that is a simple list of Operation Call)
- Press Next;
- Change the program's name to MyFirstProgram; press Finish.
- In the Program List, select the program you just created.
- Select the Program view, then press New. This will bring up the New Operation Call wizard;
- Change the name to Deploy Arm, then press Next;
- Select the roboticArm sub-system as the system we want to use:
- Under Variable, select rover;
- Under Sub-Type, select integratedRoboticArm→roboticArm;
- Now lets select the operation we want to call:
- Under Operation, select moveTo(EDouble, EDouble, EDouble, EDouble), then press Next;
- Lets set the operation parameters (here the destination joint angles values):
- In the left end side, select the first argument (turretAngle) and type its value (0.0 degrees) in the Value field on the right.
- Repeat the previous step for each of the arguments:
- shoulderAngle = 0.0 degrees
- elbowAngle = -90.0 degrees
- wristAngle = 0.0 degrees
- Save the session by pressing the Save button in the top menu.
- Test you command by pressing Invoke!
Browsing the Data Product
Up to now, we have been issuing commands, but we have not been looking at the Data Product (i.e. return value) generated by the Operation Calls. Lets do that now:
- Open the Data Products perspective if not already opened:
- In the top menu bar, select Open New Perspective. This will open the Add Perspective pop-up.
- In the pip-up, select the Data Products perspective;
- Press OK.
- In the Data Products Search, select the first Start operation call.
- The Data Products Details view now shows the metadata associated with the result of the operation call such as:
- The Context that was active when the call was made;
- The name and description that have been associated with result;
- The Relative pose of the result relative to the System that executed the call;
- The absolute pose of the result relative to the active Worksite;
- The time at the reception of the result;
- The Data Products Value Details now show the actual value return (in our case, a Boolean value).
The User Interface
Perspectives
Overview
Apogy makes use of the Perspective concept as defined in Eclipse. A Perspective is a group of Views that are related to each other or are used together for a given task. In Apogy:
- Only one Perspective is active at any given time.
- Multiple Perspectives can have multiple instance of the same View (in general).
- Users can create custom Perspectives on the fly .
- Custom Perspective can be exported / imported as a way to shared them between users.
Perspective are accessed from the main menu to open, create and select the active perspective.
Apogy Perspectives
Apogy provides a few Perspectives that are used for basics functions:
| Name | Description | Included Views | View Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welcome | Default perspective that is shown when you first launch Apogy. | Welcome | Show the welcome message for Apogy. |
| Projects | View used to create / load / import and export Sessions. | ||
| Systems | Perspective used to defined Variables, Contexts and Initial Conditions. | Variables | View used to display, create and delete Variables. |
| Contexts | View used to display, create, edit, delete and activate Contexts. | ||
| Initial Conditions | View used to display, create, edit, delete, collect and apply Initial Conditions. | ||
| Runtime | View used to display the instances of each of the Variable's System and type members. | ||
| Programs | Perspective used to define Program Groups and Programs. | Programs | View used to display, create and delete Program Groups and Programs. |
| Program | View used to edit and invoke a Program and its Operation Calls. | ||
| Runtime | View used to displays the instances of each of the Variable's System and type members. | ||
| Arguments | View used to edit the selected Operation Call arguments. | ||
| Documentation | View used to display documentation associated with the selected Operation Call or Operation Calls arguments. | ||
| Earth Surface Worksite | Perspective used to create / edit Earth Surface Worksites. | Earth Surface Worksites | Show the list of available Earth Surface Worksites and allows the user to create / import / export / delete and activate Earth Surface Worksites. |
| Maps | View used to create / edit and delete the Maps contained in a Earth Surface Worksites. | ||
| Digital Elevation Maps (DEMs) | View used to create / edit / delete CartesianTriangularMeshURLMapLayerin the selected Map of a Earth Surface Worksite. Also used to edit the appearance of Image Layers that are applied to the CartesianTriangularMeshURLMapLayer. | ||
| Image Layers | View used to create / edit / delete Image Layer for the selected Map of a Earth Surface Worksite. | ||
| Feature Of Interest | View used to create / edit / delete FeatureOfInterest Layers for the selected Map of a Earth Surface Worksite. | ||
| Other Layers | View used to create / edit / delete other layers for the selected Map of a Earth Surface Worksite. | ||
| Earth View | Perspective used to display the Earth as a whole. Used for displaying orbits and flying vehicle trajectories. | Earth View | Show the Earth as a whole together with the Earth View Layers that have been defined in the active Earth View Configuration. |
| Earth View Configuration | View used to create / edit and delete Earth View Layers used in the active Earth View Configuration. | ||
| Time Sources | Perspective used to create / edit / delete TimeSources used in the Session. | Time Sources | Displays the list of available TimeSource and provided support to create / edit / delete and set the Session active TimeSource. |
| Time Source Details | View used to display and edit the selected TimeSource details. | ||
| Data Products | Perspective used to display / create / edit and delete Data Products. | Data Products Search | Displays the list of available Data Products and provided support to create / edit / delete and search the list of Data Products. |
| Data Product Details | View used to display the details of the selected Data Products in the Data Products Search view. | ||
| Data Product Value Details | View used to display the details of the value contained in the selected Data Products. | ||
| 3D Viewing | Perspective used to display the environment in 3D. | 3D Viewer | Displays the environment rendered in 3D. |
| Node Search | Provides functions to search the environment topology for particular Nodes. | ||
| Node Presentation | View used to display the Node Presentation for the selected Node (selected in the Node Search or the Topology Tree). | ||
| Topology Tree | View used to display the topology tree and the details of the selected Node. | ||
| Node Distance | View used to display the relative position/orientation and distance between two selected Node. | ||
| Earth Atmosphere | Perspective used to create / edit Earth Atmosphere Worksites. | Earth Atmosphere Worksites | Show the list of available Earth Atmosphere Worksites and allows the user to create / import / export / delete and activate Earth Atmosphere Worksites. |
Additional plug-ins may contribute more Perspectives (such as the Apogy Example plug-ins) that provide System specifics views that are use to control and monitor specific Systems.
The Welcome Perspective
This is the default perspective that is shown when you first launch Apogy. If provides basic information about yout installation of Apogy and access to the Sessions.
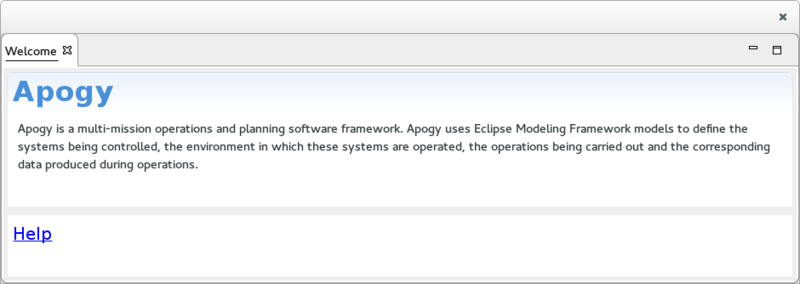
The Welcome View
The Welcome View show the welcome message of Apogy. It is divided into 2 sections:
- On the top, the Apogy section displays the description of Apogy.
- On the bottom, the Help section displays the help of Apogy.
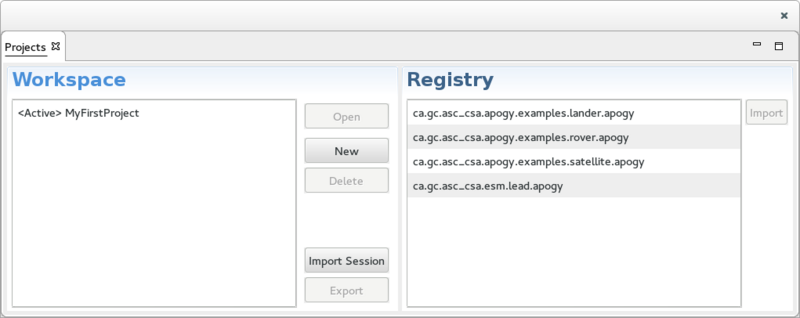
The Projects View
The Projects View shows the Sessions available. It is divided into 2 sections:
- On the left, the Workspace section displays the list of Sessions projects that are currently in the Apogy workspace. This section includes 5 buttons:
- The Open button is used to open the selected Session.
- The New brings up a Wizard to create a new Session from scratch.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Session.
- The Import button brings up a Wizard used to import archived Session into the Apogy workspace.
- The Export button brings up a Wizard used to export the selected Session to an archive.
- On the right, the Registry section displays the list of registered Sessions contributed by the installed plug-ins. This section includes one button:
- The Import button brings up a Wizard used to import the selected registered Session into the Apogy workspace.
The Systems Perspective
The Systems Perspective is used to defined Variables, Contexts and Initial Conditions.
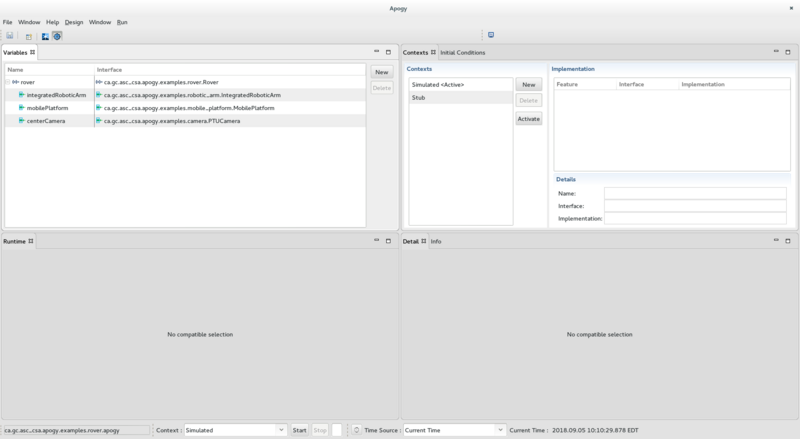
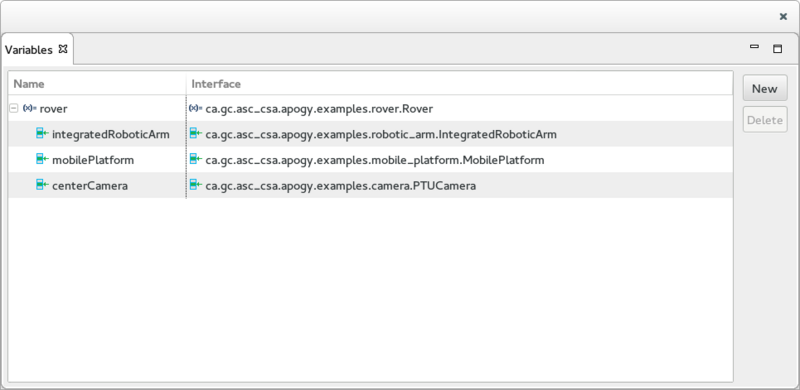
The Variables View
The Variables View is used to display, create and delete Variables.
- The left end side displays the variables defined in the Session. For composite systems, the tree shows all of the System's System Type Members. This section includes 2 buttons:
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Variable.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Variable.
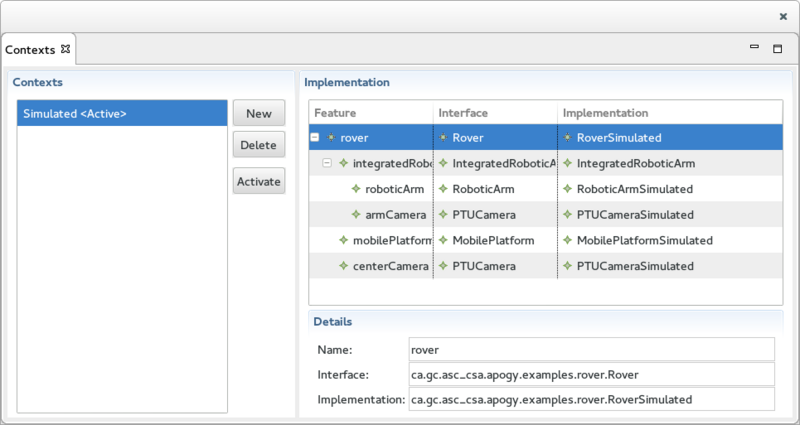
The Contexts View
The Contexts View is used to display, create, edit, delete and activate Contexts. It is divided in 3 sections:
- On the left, the Contexts section displays the list of Contexts available in the Session. The section includes 3 buttons:
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Context.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Context.
- The Activate button makes the selected Context the Session's active Context.
- On the top right, the Implementation section displays the System Interface Class for each of the Variable and, when applicable, the Variable's type members. The System Interface Class of a Variable (or a Variable's type member) can be changed by clicking in the Implementation column : a pull down menu then shows the available implementation class for the System Interface Class.
- On the bottom right, the Details section displays the details of the selected Variable or Variable's type member.
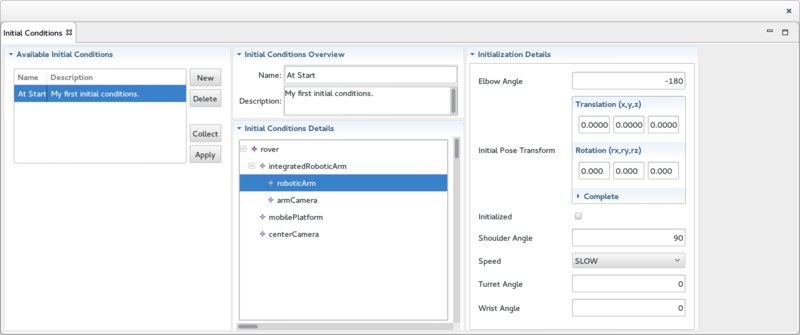
The Initial Conditions View
The Initial Conditions View used to display, create, edit, delete, collect and apply Initial Conditions. It is divided into 4 sections:
- On the left, the Available Initial Conditions section displays the list of Initial Conditions available in the Session. The section also includes 4 buttons:
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Initial Conditions.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Initial Conditions.
- The Collect button collect the Session System's states and saves them to the selected Initial Conditions.
- The Apply button applies the selected Initial Conditions to the Session System's.
- In the center, on the top, the Initial Conditions Overview section displays an overview of the selected Initial Conditions.
- In the center, on the bottom, the Initial Conditions Details section provides the details of the Initial Conditions for each Variable.
- On the right, the Initialization Details section provide display and edit function for the element of the Initial Conditions selected in the Initial Conditions Details section.
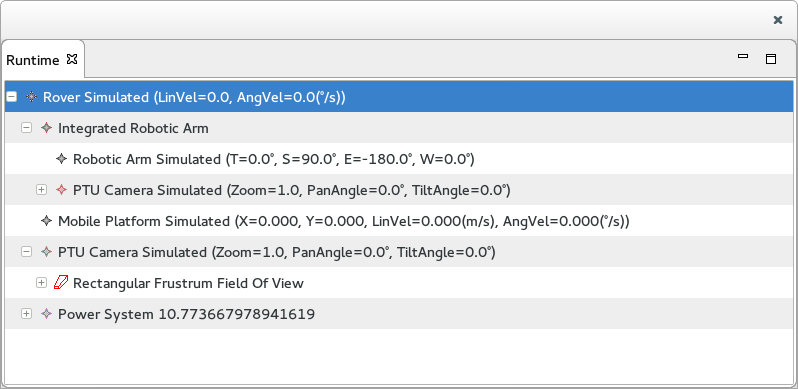
The Runtime View
The Runtime View displays the instances of each of the Variable's System and type members. Note that this view is populated only after the Variables are instantiated.
The Programs Perspective
This perspective is used to display, create and edit Program Groups and Programs.
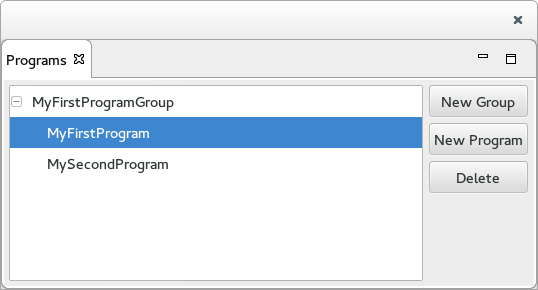
The Programs View
The Programs View is used to display, create and delete Program Groups and Programs.
- The tree viewer on the left displays the list of available Program Group and the Program they contain.
- The right end side includes 3 buttons:
- The New Group button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Program Group.
- The New Program button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Program.
- The Delete button deletes the Program Group or Program selected. Note that deleting a Program Group also deletes the Programs it contains.
The Program View
The Program View is used to edit and invoke Programs. Currently, Operation Call List and Java Script Program are supported. Depending on the type of Program, this view displays different elements.
In both case, the tool bar includes a Run action to execute the Program.
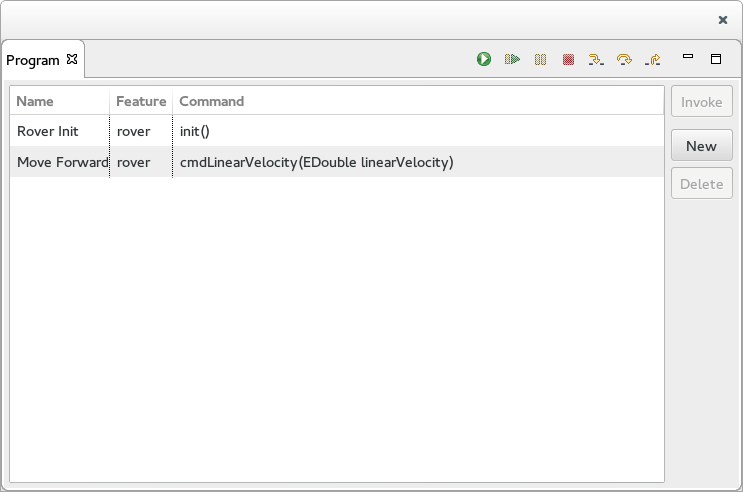
The Program View - Operation Call List
When the Program selected in the Programs View is an Operation Call List, the view display the list of Operation Call.
- The table on the left displays the list of Operation Call contained in the selected Operation Call List.
- The right end side includes 3 buttons:
- The Invoke button triggers the execution of the selected Operation Call.
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Operation Call.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Operation Call.
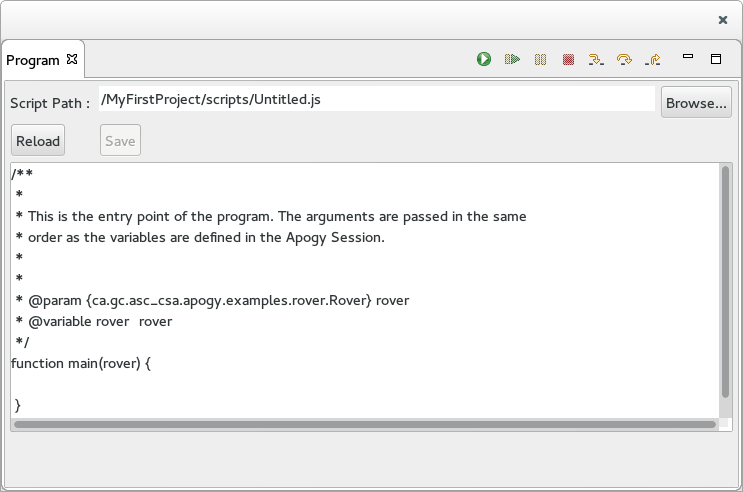
The Program View - Java Script Program
When the Program selected in the Programs View is a Java Script Program, the view display the source code of the script.
- The full path of the script is display at the top.
- The Browse... button bring up a File Selection Wizard used to set the path to the file containing the script.
- The Reload button force the script file to be reloaded.
- The Save button saves the displayed source code of the script to the file.
- The bottom text editor allow the script source code to be displayed and edited.
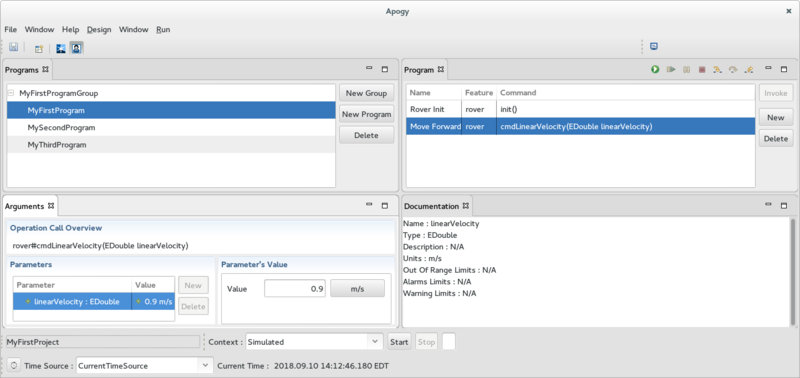
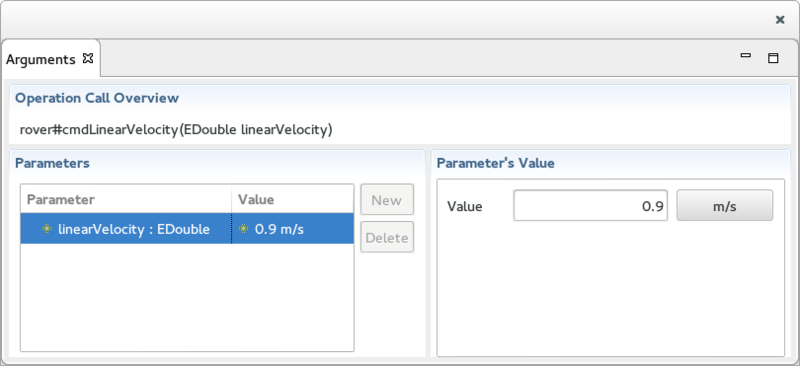
The Arguments View
The Arguments View is used display the selected Operation Call arguments and edit their values. It is divided into 3 sections:
- At the top, the Operation Call Overview displays a summary of the Operation Call being edited.
- At the bottom:
- On the left, the Parameters section displays the name and type of the argument in the first column and its associated value in the second column.
- On the right, the Parameter's Value section allows the selected Parameter to be edited.
The Documentation View
The Documentation View is used to display documentation associated with the selected Operation Call or Operation Calls arguments.
The documentation presented is the one that was defined in the XCore model of the System Interface Class.
The Earth Surface Worksite Perspective
The Earth Surface Worksite Perspective is used to create and edit Earth Surface Worksites.
The Earth Surface Worksites View
The Earth Surface Worksites View displays the list of available Earth Surface Worksites and allows the user to create / import / export / delete and activate Earth Surface Worksites. It includes 3 sections:
- On the left, the Earth Surface Worksites section displays the list of Earth Surface Worksites currently available. This section includes 5 buttons:
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Earth Surface Worksite.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Earth Surface Worksite.
- The Active button make the selected Earth Surface Worksite the Session's active Worksite.
- The Import button brings up a Wizard used to import a Earth Surface Worksite from a file.
- The Export button brings up a Wizard used to export the selected Earth Surface Worksite to file.
- On the left, at the top, the Worksite Origin section displays the geographical coordinates of the origin and the azimuth of the X axis of the selected Earth Surface Worksite.
- On, the left, at the bottom, the Worksite Details section displays the details of the selected Earth Surface Worksite.
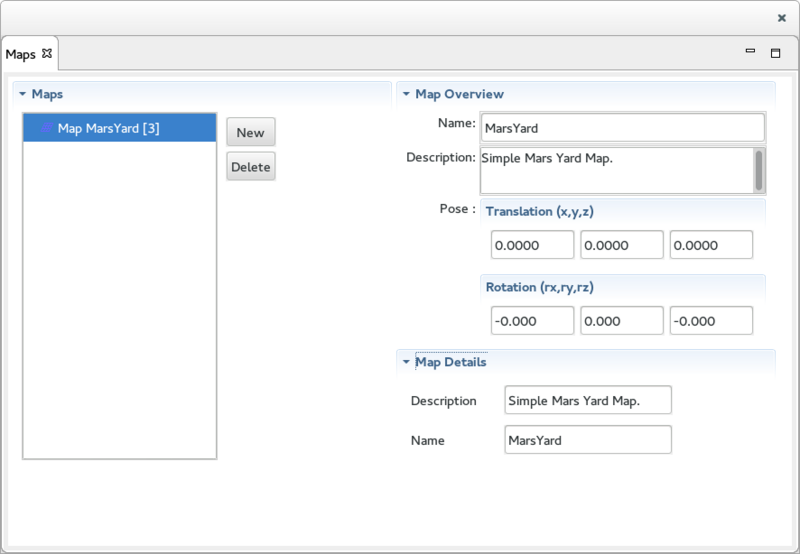
The Maps View
The Maps View is used to create / edit and delete the Maps contained in a Earth Surface Worksites. It includes 3 sections:
- On the left, the Maps section displays the list of Map that are defined in the selected Earth Surface Worksite. This section includes 2 buttons:
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Map.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Map.
- On the right, at the top, the Map Overview section displays an overview of the selected Map (including its transform to the worksite origin).
- On the right, at the bottom, the Map Details section displays the details of the selected Map.
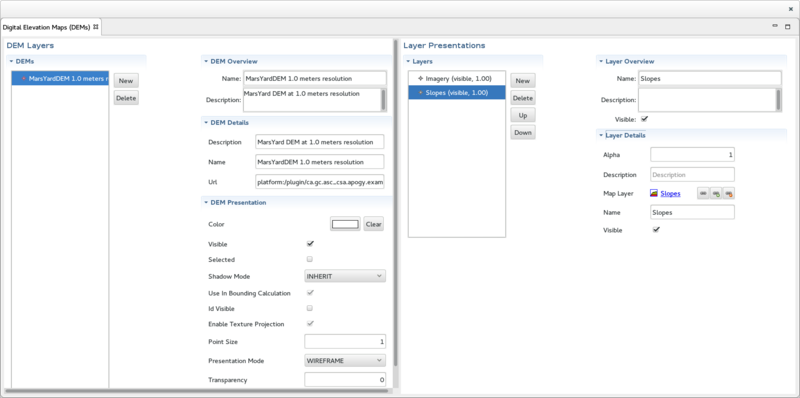
The Digital Elevation Maps View
The Digital Elevation Maps View displays the Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layers contained in the selected Map. It is divided into 2 main sections:
- On the left, the Earth Surface Worksites section is used to display the Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layers and edit their properties. This section is sub-divided into 4 sub-section:
- On the left, the DEMs section display the list of Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layers found in the selected Map.
- On the right, at the top, the DEM Overview display an overview of the selected Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layer.
- On the right, in the middle, the DEM Details display the details of the selected Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layer.
- On the right, at the bottom, the DEM Presentation display the Node Presentation associated with the selected Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layer.
- On the right, the Layer Presentations section displays the Image Layer Presentation that is associated with the selected Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layer. This section sub-divided into 3 sub-section:
- On the left, the Layers section displays the list of Image Layer Presentation associated with the selected Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layer.
- On the right, at the top, the Layer Overview section display an overview of the selected Image Layer Presentation.
- On the right, at the bottom, the Layer Details display the details of the selected Image Layer Presentation. Editing the Image Layer Presentation attributes will change the appearance of the image layer projection onto the selected Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layer.
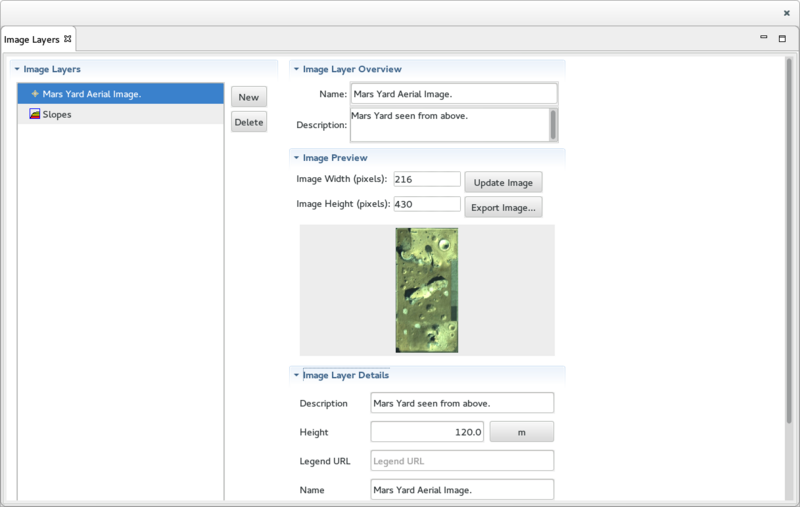
The Image Layers View
The Images Layers View displays the list of Image Layers that are associated with the selected Triangular Mesh Layers. It is divided into 4 sections:
- On the left, the Image Layers section displays the list of Image Layers that are associated with the selected Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layers. This section includes 2 buttons:
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Image Layer.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Image Layer.
- On the right, at the top, the Image Layer Overview section display an overview of the selected Image Layer.
- On the right, in the middle, the Image Preview section display a preview image of the Image Layer, and includes 2 buttons:
- The Update Image button updates of the image of the Image Layer.
- The Export Image button brings up a Wizard used to export the selected Image Layer 's image to a file.
- On the right, at the bottom, the Image Layer Details section display the details of the selected Image Layer.
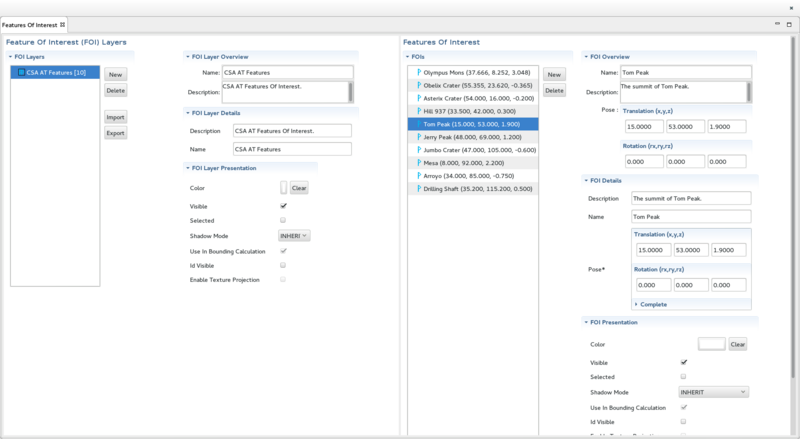
The Features Of Interest View
The Features Of Interest View displays the list of Features Of Interest Layers available in the selected Map. It is divided into 2 main sections:
- On the left, the Features Of Interest (FOI) Layers. This section is sub-divided into 4 sub-sections:
- On the left, the FOI Layers section display the list of Features Of Interest Layers available in the selected Map. It includes 4 buttons:
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Feature Of Interest Layer.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Feature Of Interest Layer.
- The Import button brings up a Wizard used to import a Feature Of Interest Layer from a file.
- The Export button brings up a Wizard used to export the selected Feature Of Interest Layer to a file.
- On the right, at the top, the FOI Layer Overview displays an overview of the selected Features Of Interest Layer
- On the right, in the middle, the FOI Layer Details displays the details of the selected Features Of Interest Layer
- On the right, at the bottom, the FOI Presnetation displays the details of the Node Presentation associated with the selected Features Of Interest Layer
- On the left, the FOI Layers section display the list of Features Of Interest Layers available in the selected Map. It includes 4 buttons:
- On the right, the Features Of Interest section display the list of Feature Of Interest contained in the selected Features Of Interest Layer. It includes 4 sections:
- On the left, the FOIs section displays the list Feature Of Interest.
- On the right, at the top, the FOI Overview displays an overview of the selected Features Of Interest
- On the right, in the middle, the FOI Details displays the details of the selected Features Of Interest
- On the right, at the bottom, the FOI Presentation displays the details of the Node Presentation associated with the selected Features Of Interest
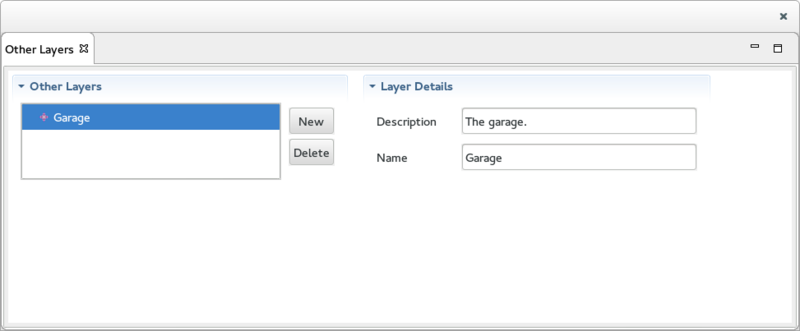
The Other Layers View
The Other Layers View is used to display / create / delete other types of Layers. It is divided into 2 main sections:
- On the left, the Other Layers section displays the list of Layers that are NOT Cartesian Triangular Mesh Layer, Image Layer or Feature Of Interest Layer.
- On the right, the Layer Details displays the details of the selected Layer
The Earth View Perspective
This perspective used to display the Earth as a whole or data that is at large scale (few kilometers). It is used for displaying orbits and flying vehicle trajectories.
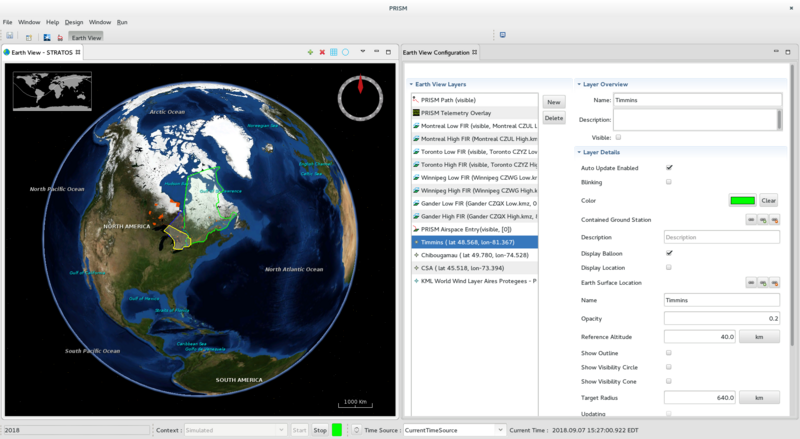
The Earth View
The Earth View shows the Earth using the active Earth View Configuration which itself contains the Earth View Layers to be shown.
The tool bar provides quick access to the 3D viewer functions. The following table describes these functions.
Note that the pull-down to the left of the tool bar provides a way to select the active Earth View Configuration.
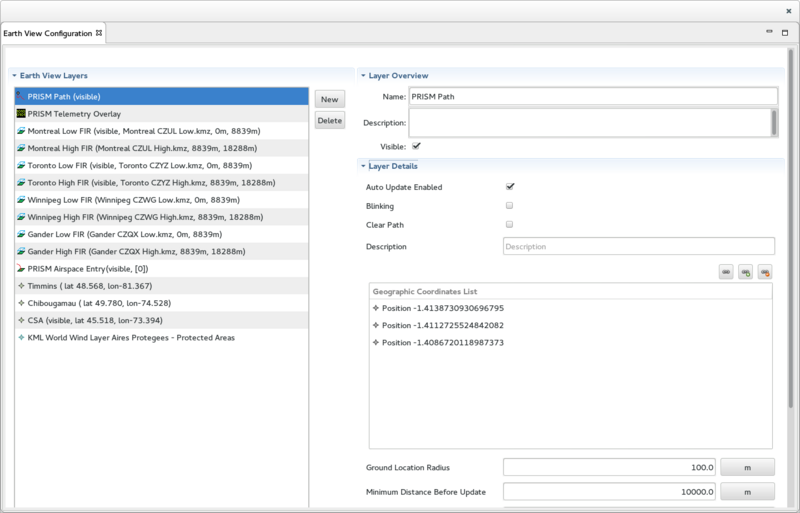
The Earth View Configuration View
The Earth View Configuration View is used to create / edit and delete Earth View Layers used in the active Earth View Configuration. It is divided into 4 sections:
- On the left, the Earth View Layers section displays the list of Earth View Layer that are defined in the selected Earth View Configuration. This section includes 2 buttons:
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Earth View Layer.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Earth View Layer.
- On the right, at the top, the Layer Overview section displays an overview of the selected Earth View Layer.
- On the right, at the bottom, the Layer Details section displays the details of the selected Earth View Layer.
The Time Sources Perspective
This perspective is used to display, create, delete and edit Time Sources that are used to feed the time to the active Session.
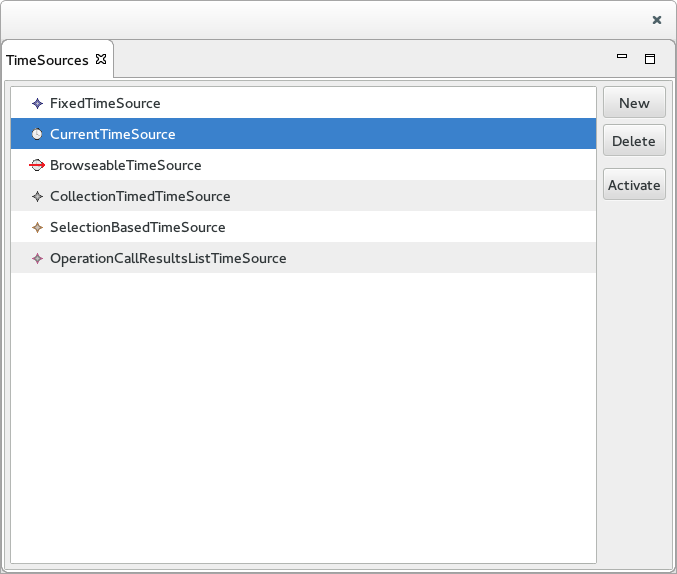
The Time Source View
The Time Source View is used to display the list of available Time Source. It includes:
- On the left, the Time Source section displays the list of Time Sources that are defined in the Session. This section includes 3 buttons:
- The New button brings up a Wizard used to create a new Time Source.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Time Source.
- The Activate button sets the selected Time Source as the active Time Source for the Session.
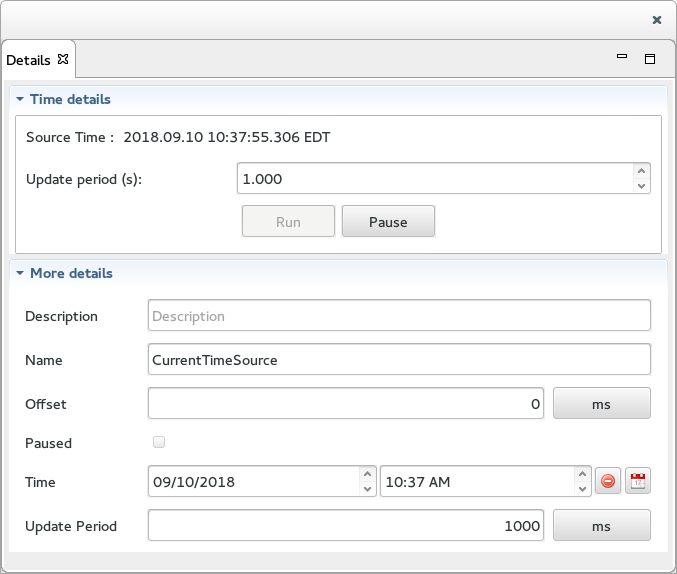
The Time Source Details View
The Time Source Details View is used to display and edit the attributes of the selected Time Source. It is divided into 2 sections:
- At the top, the Time Details section displays a Time Source dependent summary used to control the selected Time Source. This display is custom to each of the supported Time Source.
- At the bottom, the More Details section displays more details about the selected Time Source.
The Data Products Perspective
The Data Products Perspective is used to display / create / edit and delete Data Products.
The Data Products Search View
The Data Products Search View displays the list of available Data Products and provides support to create / edit / delete and search the list of Data Products. It is divided into 2 sections:
- At the top, the Filters and Sorters section provides controls to create and configure filters and sorters. It is divided into 2 sections:
- On the left, the Filters section provides controls to create and configure filters. Filters are used to narrow down the search.
- On the right, the Sorters section provides controls to create and configure sorters. Sorters are used to sort the Data Products that pass through the Filters.
- At the bottom, the Data Products section displays the list of Data Products that have passed the filters, sorted according to the sorters used. This section includes 2 buttons on the right:
- The New button bring up a Wizard used to create a Data Product.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Data Product.
The Data Product Details View
The Data Product Details View is used to display the details of the selected Data Products in the Data Products Search view. It is divided into 2 sections:
- At the top, the Product Details displays the metadata associated with the Data Product (Time stamp, location, description, etc.).
- At the bottom, the Operation Call Details displays the information about the Operation Call that created the Data Product(Variable, EOperation, Parameters, etc.).
The Data Product Value Details View
The Data Product Value Details View is used to display the details of the value contained in the selected Data Product.
It includes the actual return value data. Depending on the type of the return value, an Export Data Product To File... button may be available. This button brings up an Export Wizard used to export the selected Data Product value to file(s).
The 3D Viewing Perspective
This perspective is used to display the environment in 3D. It includes a 3D rendering of the world and control over the rendering settings of the Nodes composing the Apogy topology.
The 3D Viewer
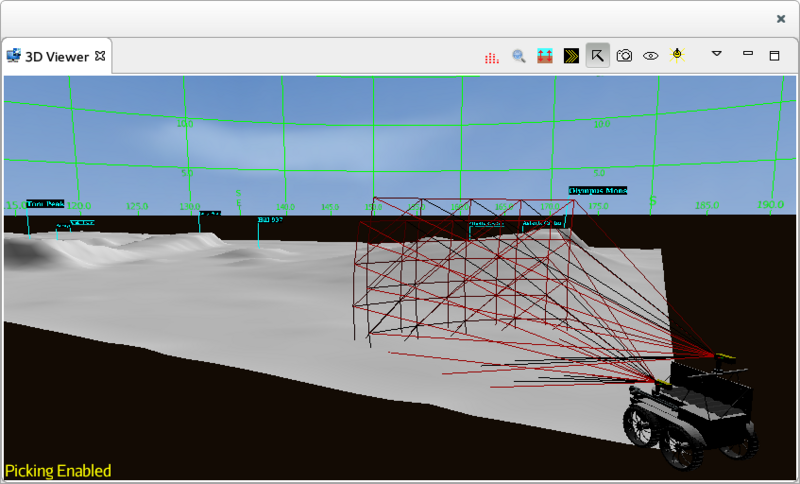
The 3D Viewer displays the environment rendered in 3D.
Navigating the 3D world is done using the mouse. The movement of the mouse change the position and orientation of the view point.
The following table identifies the buttons and mouse motion used to move the viewpoint:
| Button | Mouse Motion | Viewpoint Motion |
|---|---|---|
| Center | Forward | Moves forward |
| Back | Moves backward | |
| Left | Forward | Rotates down |
| Back | Rotates up | |
| Left | Rotates left | |
| Right | Rotates right | |
| Right | Forward | Moves down |
| Back | Moves Up | |
| Left | Moves left | |
| Right | Moves right |
The tool bar provides quick access to the 3D viewer functions. The following table describes these functions.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| |
Toggles the display of the 3D rendering statics (frame rate, number of vertices, number of triangles, etc.) on top of the view. |
| Triggers a move forward / back of the view point to bring all the 3D element into view. | |
| Triggers a change in the view point orientation to bring it to the horizontal. | |
| Toggles the translation speed between the low and high speed factors. This determine how quickly the view point position changes for a given motion of the mouse. | |
| Toggles the picking mode. When enabled, the mouse navigation is disabled, and clicking on the left button triggers a selection in the 3D viewer. The words 'Picking Enabled' appears in yellow on the lower left corner of the view. | |
| Trigger a screen capture of the 3D display and bring-up a File Selection Wizard use to specify where to save the image. | |
| Bring-up a Wizard used to create / edit / delete View Points. | |
| Toggles between the lighting provided by the Worksite to a pre-defined ambient light providing uniform lighting. |
Note that the pull-down to the left of the tool bar provided a way to select the active View Point.
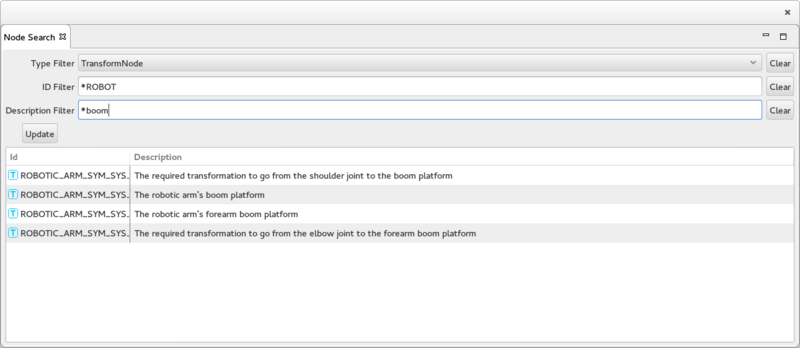
The Node Search View
The Node Search View provides functions to search the environment topology for particular Nodes. The view provides 3 filters that can be combined to narrow down the search.
- On the top are located the 3 filters input:
- The Type Filter provides a pull-down menu used to select the type of Node the user is looking for. The Clear button clears the Type Filter (all type Node passes the filter).
- The ID Filter is used to provide a filter on the Node ID. It can include wildcard (*). The Clear button clears the ID Filter (all Node ID passes the filter).
- The Description Filter is used to provide a filter on the Node description. It can include wildcard (*). The Clear button clears the Description Filter (all Node description passes the filter).
- In the middle, the Update button cause the filter to be applied and the Node list to be updated.
- At the bottom, a table shows the Nodes that have passed the filters.
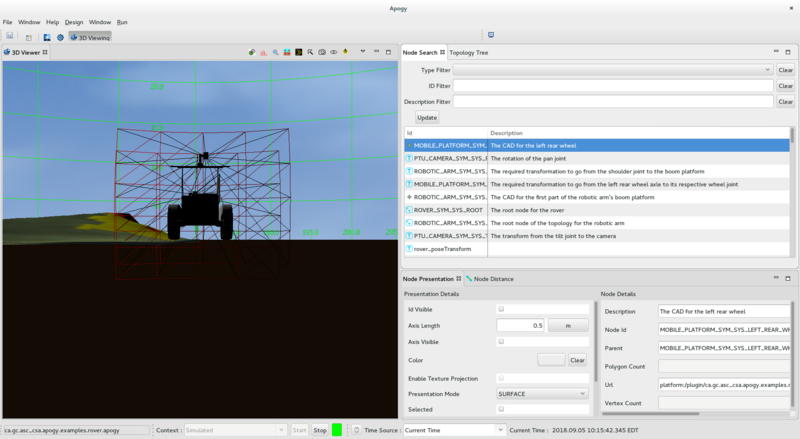
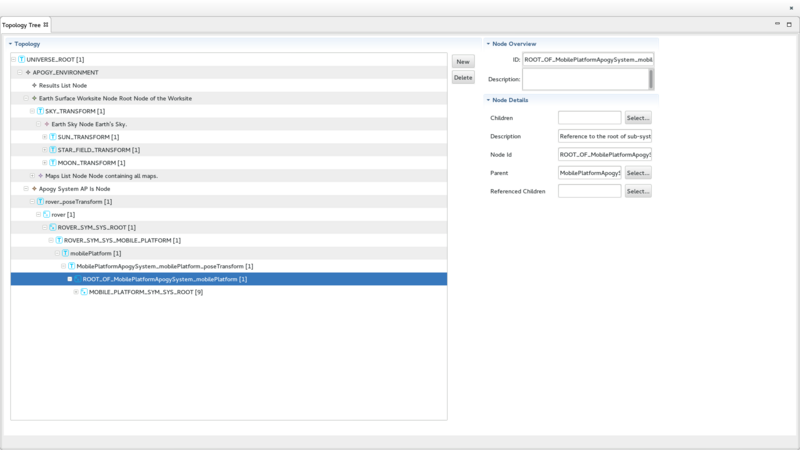
The Topology Tree View
The Topology Tree View is used to display the topology tree and the details of the selected Node. It is divided into 3 sections:
- On the left, the Topology section includes a tree viewer displays the Apogy topology. This section also includes 2 buttons:
- The New button brings-up a Wizard used to create a Node. The Node will be created under the Node currently selected in the tree.
- The Delete button deletes the selected Node (and the Node's children).
- On the right, at the top, the Node Overview section provides a summary of the selected Node.
- On the right, at the bottom, the Node Details section provides the details of the selected Node. It can be used to edit the Node attributes.
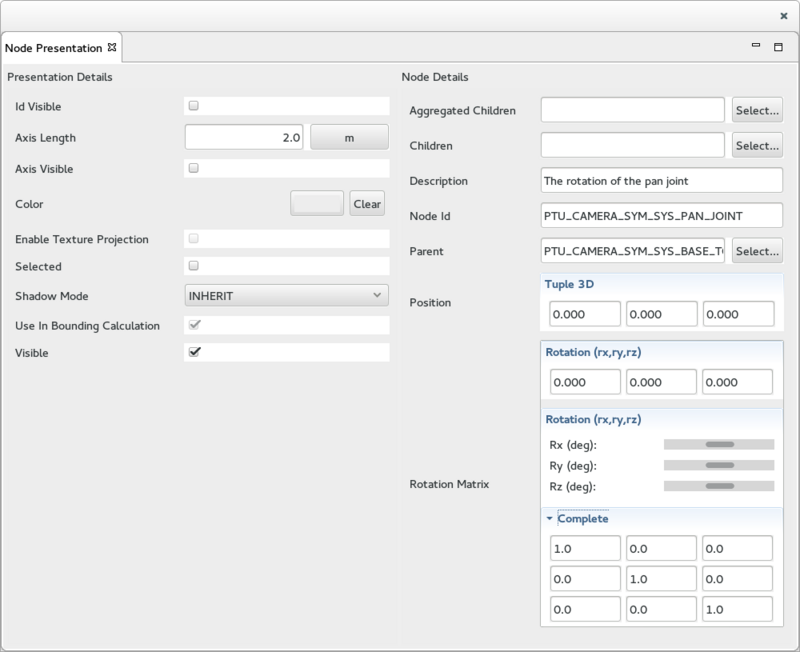
The Node Presentation View
The Node Presentation View is used to display and edit the Node Presentation for the selected Node (selected in the Node Search view or the Topology Tree view). It is divided into 2 sections:
- On the left, the Presentation Details section provides the details of the Node Presentation associated with the selected Node. It can be used to edit the presentation attributes.
- On the right, the Node Details section provides the details of the selected Node. It can be used to edit the Node attributes.
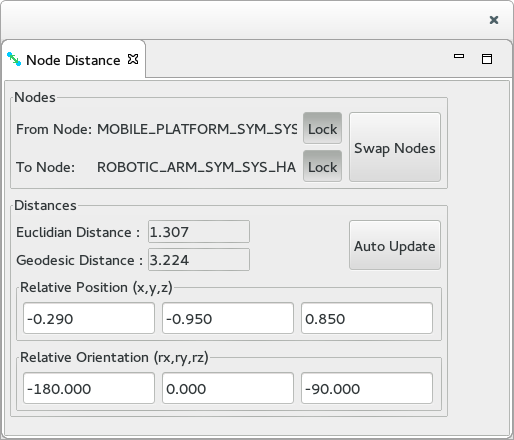
The Node Distance View
The Node Distance View is used to display the relative position/orientation and distance between two selected Nodes. This view reacts to selection of Node in either the Node Search View or the Topology Tree View. It is divided into 2 sections:
- At the top, the Nodes section displays the 2 Nodes that have been selected. This section includes 3 buttons:
- Two Lock buttons that locks the selected from / to Node (i.e. when locked, the Node will no longer be updated when a new Node is selected).
- The Swap Nodes switch the Nodes around (i.e. the From Node become the To Node and vice-versa).
- At the bottom, the Distances section displays the distance. between the selected node:
- The Euclidian Distance displays the 3D straight line distance, in meters.
- The Geodesic Distance displays the distance separating the 2 Nodes in the topology graph, in meters. It is a measure of how far the Nodes are in the graph.
- The Relative Position displays the position of the To Node in the From Node frame of reference.
- The Relative Orientation displays the orientation of the To Node in the From Node frame of reference as Euler angles in degrees.