Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
SMILA/Project Concepts/Runtime Process and Environment
Description
Here comes the description of the requirement (functional or non-functional) .
Discussion
Technical proposal
{note}
TODO:
- Error Handling, Error-Level
- Retry Handling/Timeouts (e.g. how do we cover temporary network issues)
- Equinox Runtime (does the runtime support logging in cmd window?)
{note}
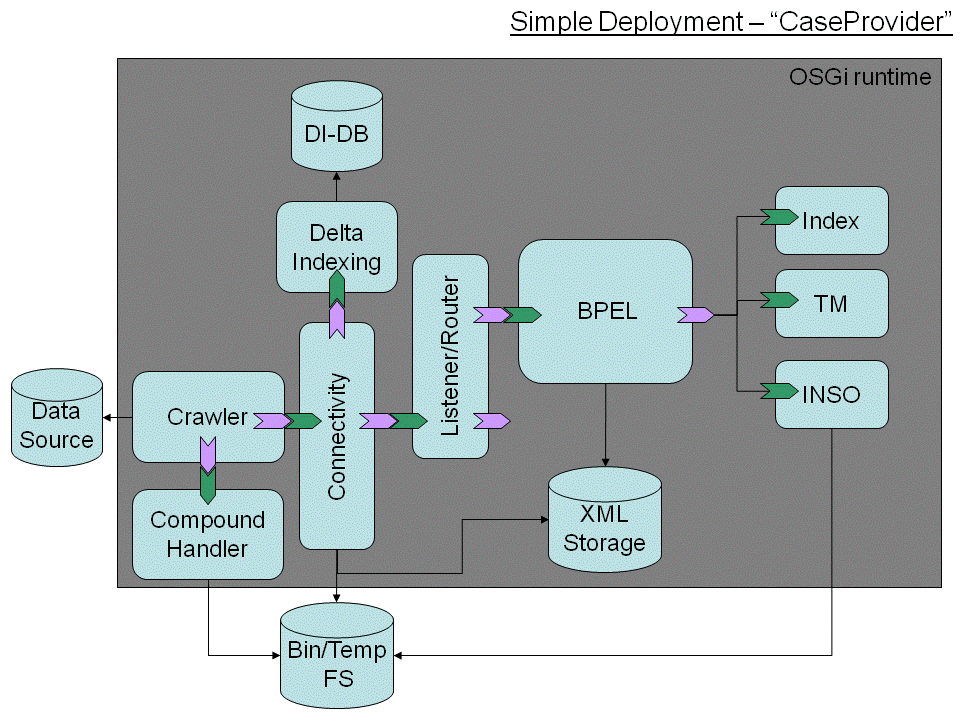
{info} This section may only be edited by assigned developer(s). His responsibility is also to reflect any agreed changes/details in discussion section.{info} An SMILA project installation could have different characteristics. First of all the SMILA project allows different information technology vendors to leverage their product development by using ready to use components. That means the SMILA is used to complete existing products.
Software installation scenarios are inspired by enterprise needs. For some of these scenarios SMILA runtime configurations/installations will be provided.
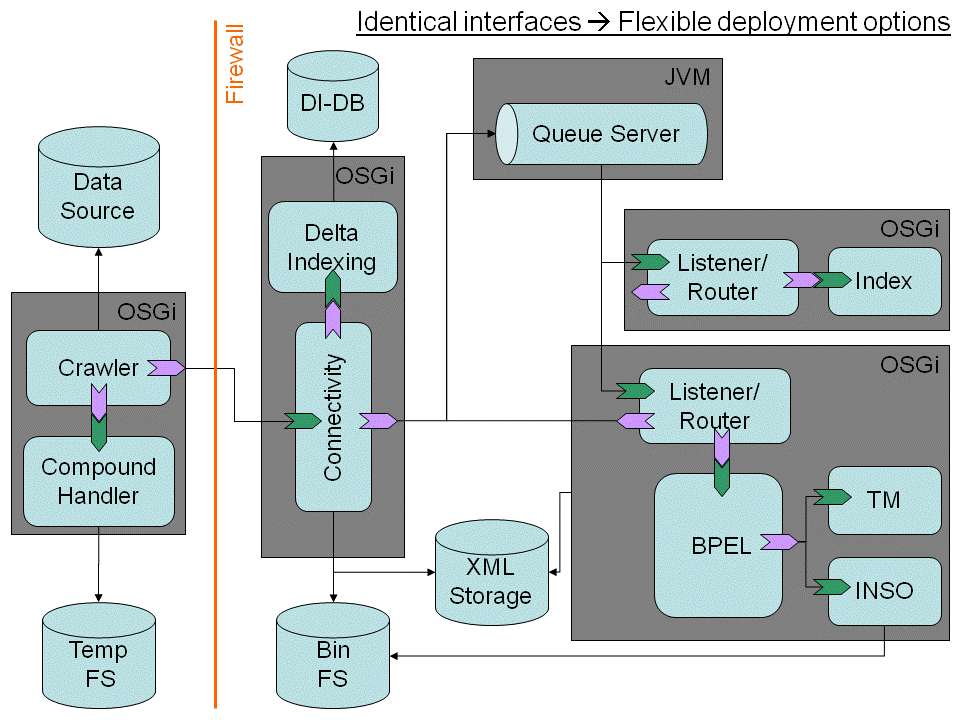
The creation of the SMILA runtime processe(s) - multiple - is leveraged by the OSGi development model.
The SMILA runtime processes will contain glue logic that is optimized for the supported business process (e.g. support for command line interface, ...). There is a strong relationship between the runtime processes and the role/functionality concept of a given node.
A role is a kind of functionality (e.g. a set of business processes) that is exposed by a node. A node is a set (1:n) of computers.
Currently we distinguish the following nodes/roles:
- Development and configuration environment
- SMILA single node installation
- SMILA search
- SMILA indexing
- IRM (simple)
- IRM (complex)
For each node a process optimized runtime is developed. These runtimes add features (e.g. command line control, communication aspects ...) to the SMILA runtime. The core functionality is derived from reusable OSGi components (e.g. BPEL, compound management, monitoring ...).
Role features
Error Handling
Crash prevention/detection
Under bad circumstances a SMILA runtime process may crash or get in an unstable state. To create a stable environment a crash prevention/detection mechanism was designed.
A controller is monitoring the SMILA runtime process for stability. If stability requirements are no longer met the process is restarted and a system event is created.
This allows a stable restart of components even in case of "Out of Memory" exceptions or other critical errors.
The restarting feature creates more reliability to the whole system. The downtime of a component is that way minimized (e. g. to reduce problem for long running conversions ...).
Role creating glue
The glue combines a set of features/bundles together to a usable and installable component that exposes the required functionality (e.g. functionality to extract data using IRMs; feature to process compounds...).
This glue must be developed for every role and is therefore not contained in the feature table.
Clustering support and application state
Several nodes require clustering for load distribution or fault tolerance.
Clustering put extended requirements for maintain application state handling to the application. Samples are:
- Scheduler to guarantee execution of functionality
- Load distribution
- Meta data storages
- ...
Nodes or roles are just marked whether they are requiring clustering support.
Monitoring
The monitoring feature allows external software (e.g. network monitoring tools) to monitor the application.
Command Line Interface
A command line interface for controlling exposed functionality.
Graphical User Interface
Description of a graphical user interface that is able to control functionality in the system.
Web Service Access
The web service access feature is responsible for exposing data or functionality to external components.
Remote Configuration
The remote configuration feature describes whether it's required to change system configuration from a remote location.
Authentication
The authentication feature describes whether the component requires authentication support to be accessed from a remote/local location.
Encryption
The encryption feature describes whether encryption functionalities must be implemented.
Node types/roles
Development and Configuration Environment
The development and configuration environment is used by consultants or by developers to configure/develop the SMILA system.
Based on process requirements different feature areas are available:
- Development of IRMs
- BPEL process description
- IRM configuration
- Debugging of information annotation
- ...
| Feature | Yes/no/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Error handling | ||
| Crash prevention/detection | NO | |
| Clustering | NO | |
| Monitoring | ||
| Command Line Interface | NO | |
| Graphical User Interface | ||
| Web Service Access | NO | |
| Remote Configuration | NO | |
| Authentication | ||
| Encryption |
SMILA single node installation
The single node installation is the smallest and easiest SMILA installation. It should be able to be integrated in an external application. Search, indexing and a simple user interface is provided.
The ability to do a easy migration to larger installations must be available.
| Feature | Yes/no/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Error handling | ||
| Crash prevention/detection | YES | |
| Clustering | NO | |
| Monitoring | YES | |
| Command Line Interface | YES | |
| Graphical User Interface | ||
| Web Service Access | YES | |
| Remote Configuration | NO | |
| Authentication | YES | |
| Encryption | YES |
SMILA search
The SMILA search is optimized node for search processing. This node is easy to scale over different computer.
Performance in area of throughput is extreme important.
| Feature | Yes/no/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Error handling | ||
| Crash prevention/detection | ||
| Clustering | ||
| Monitoring | ||
| Command Line Interface | ||
| Graphical User Interface | ||
| Web Service Access | ||
| Remote Configuration | ||
| Authentication | ||
| Encryption |
SMILA indexing
The SMILA indexing is optimized for indexing operations.
| Feature | Yes/no/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Error handling | ||
| Crash prevention/detection | ||
| Clustering | ||
| Monitoring | ||
| Command Line Interface | ||
| Graphical User Interface | ||
| Web Service Access | ||
| Remote Configuration | ||
| Authentication | ||
| Encryption |
IRM (simple)
The IRM (simple) is a simple installation.
The installation is just able to send information to the SMILA. No other runtime features are available.
| Feature | Yes/no/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Error handling | ||
| Crash prevention/detection | ||
| Clustering | NO | |
| Monitoring | ||
| Command Line Interface | ||
| Graphical User Interface | NO | |
| Web Service Access | ||
| Remote Configuration | NO | |
| Authentication | ||
| Encryption |
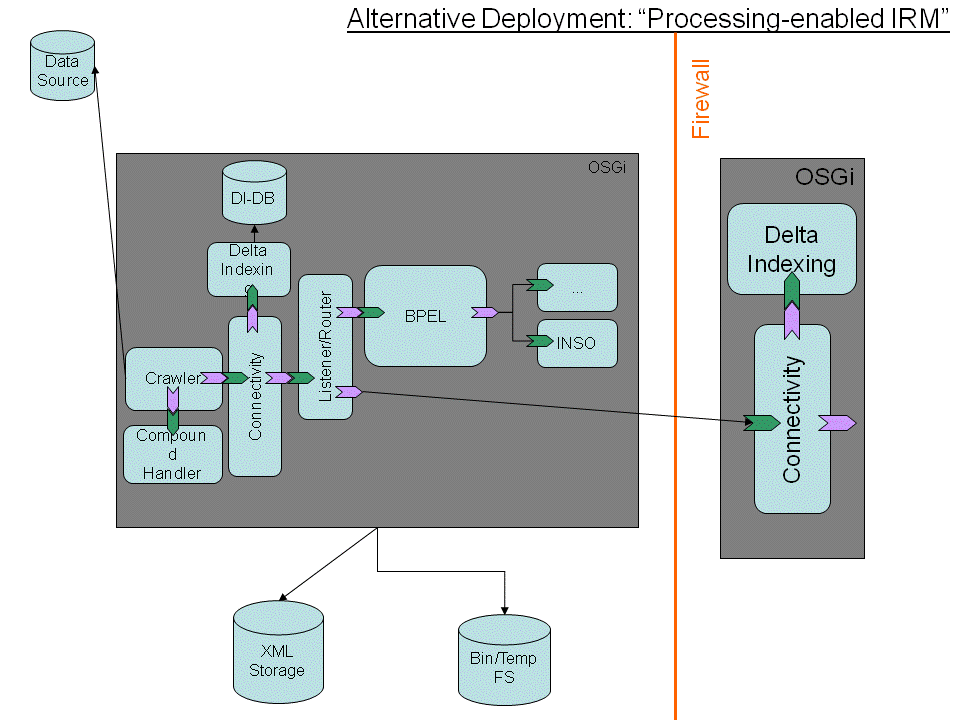
IRM (complex)
The IRM (complex) installation is an installation providing a huge set of IRM and data related functionalities to the node installation. (e.g. data annotation, generation indexing, call ability via remote web services, ...)
The complex IRM installation is able to perform data related tasks to perform an communication optimization between the connected main node and the IRM endpoint.
| Feature | Yes/no/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Error handling | YES | |
| Crash prevention/detection | YES | |
| Clustering | Optional | |
| Monitoring | YES | |
| Command Line Interface | YES | |
| Graphical User Interface | Optional | |
| Web Service Access | YES | |
| Remote Configuration | YES | |
| Authentication | YES | |
| Encryption | YES |