Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Papyrus/Neon Work Description/NewFeature/Papyrus Refactoring Service
Contents
Papyrus Refactoring Service
Overview
An UML model can contain several files and it can reference external models. When user makes an action as rename a file, Papyrus must ensure that all references are always consistent at the end of execution.
Use Cases
- Rename Action
- Move elements between model
- Control Mode
- Externalise Profile Application
- Does the Refactoring action should be launched ?
Requirements
| Index | Description |
|---|---|
| REQ_001 | Have a central mechanism to manage Refactor operation |
| REQ_002 | Can choice the scope of the refactor resolution |
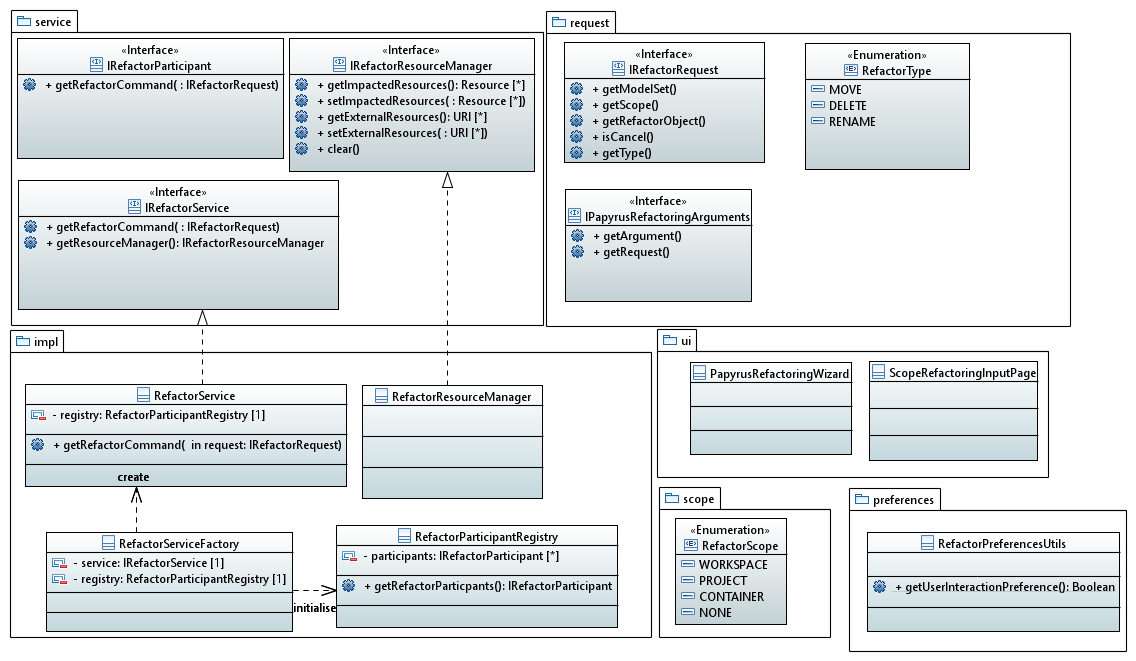
Notions
Based on Control Mode mechanism and Element Type service, the mechanism uses three notions:
| Notion | Description |
|---|---|
| Request | It contains all necessary information to execute correctly the refactor. |
| Service | It is the entry point for the mechanism and it takes Request to deliver commands. It knows all participants. |
| Participant | It registers on service to provide a command according to input request. |
| Command | It contains refactor operation. |
| Scope | It limits the refactor operation. It takes three values: None, Project, Workspace. |
Filter Participants
It is necessary to give the possibility to exclude a participant of an Refactoring action. A participant can be useful only during one kind of Refactoring Action. This type could be defined during creation of the Request and could be chosen among this set:
- ALL
- MOVE
- RENAME
Components
The new mechanism adds a new plugin to contain all engines. This new plugin exposes an extension point.
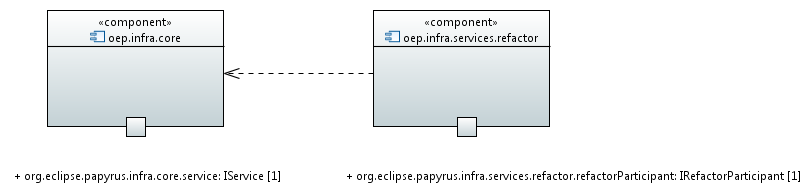
Plugin
A new plugin will be created to contain the Refactor service. To declare the service, this plugin must depend of org.eclipse.papyrus.infra.core which exposes the extension point to declare a Papyrus service. The Refactor service plugin exposes itself an extension point, org.eclipse.papyrus.infra.services.refactorParticipant to register participants of Refactor.
Extension Point
It permits to add new Participant to a refactor. This class must implement the interface IRefactorParticipant. The participant returns a command according of input request. The role of participant has to be clearly defined to know which side effect of Refactor, it resolves. The participant is dependent of its scope resolution.
User Interface
Description
The service needs to know which is the refactor scope. The scope determines from where the refactor starts. The user interface lets to user to choice between three different scopes.
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
| None | It means that refactor doesn’t need to be executed. |
| Container | It means that refactor uses all models present in container resource of the current model to resolve broken references. |
| Project | It means that refactor uses all models present in Project to resolve broken references. |
| Workspace | It means that refactor uses all model present in Workspace to resolve broken references. |
Behaviour
Triggering
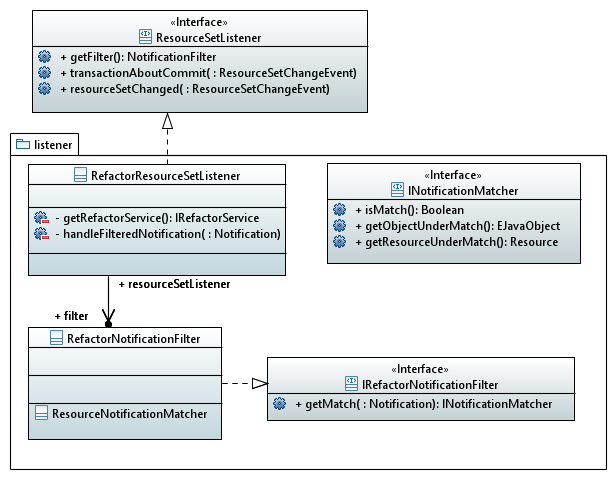
The service must be call when an element change its location. The service must be in back-end and it must be triggered by particular events. The managing of save of external modifications like model files in other project must be made through the ResourceSetListener too. The Refactoring service can not depend of LifeCycleDependency because this introduces bad dependencies for a independent service.
Conception
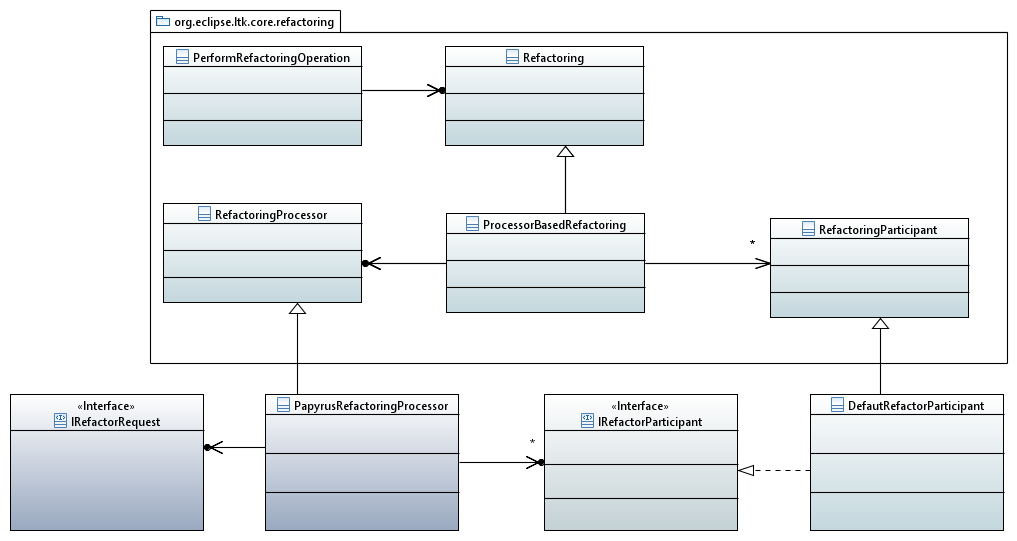
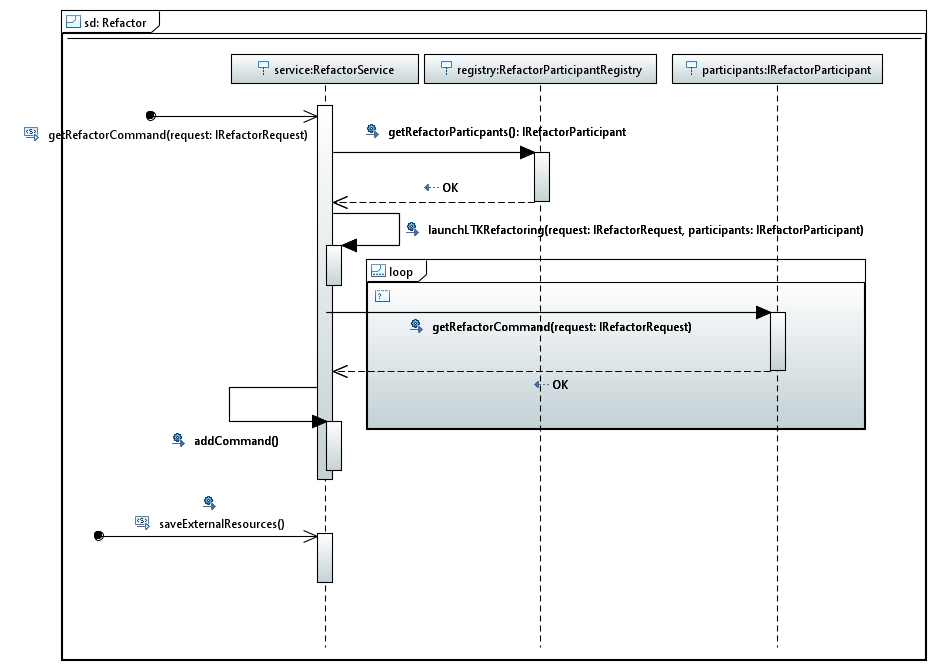
The mechanism is similar as Control Mode or Element Type Edit service. From one request and the service, this one returns a command for the refactor. The service uses LTK API to perform UI interaction and perform refactoring.
Architecture
LTK Integration
Interaction
Refactoring Resolution
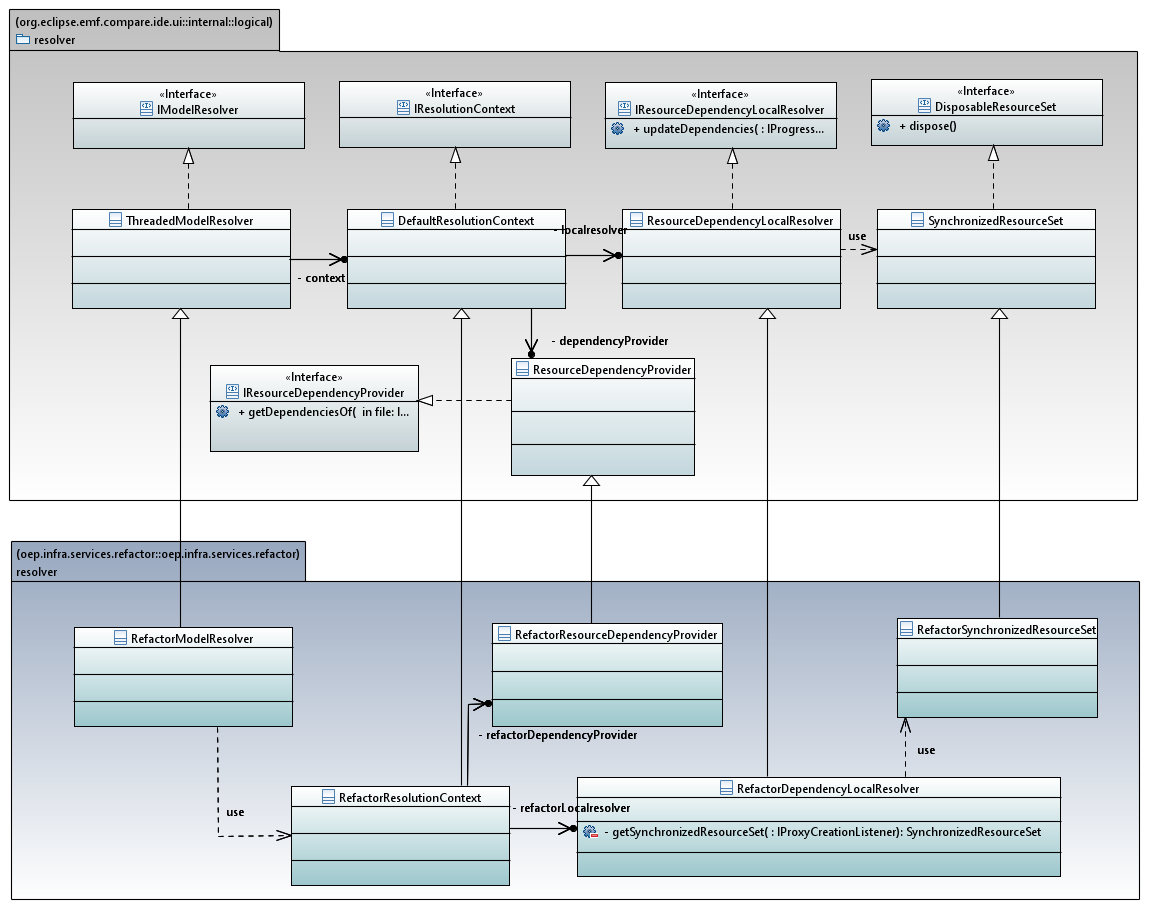
EMF Compare Integration
This integration of EMF Compare permits to use their ThreadedModelResolver with our Scope Resolution implementation.