Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Importing an Esri Shapefile
The Esri Shapefile Format
The Esri shapefile is a popular format for geographic information systems (GIS). Shapefiles can describe polygons, polylines and points. For example, polygons can represent geographical regions like countries and states while polylines can represent roads, rivers and so on. Points are currently not used in the Shapefile Graph Generator.
A shapefile is a set of various files: three of these files are used by the Shapefile Graph Generator.
- .shp — shape format; contains the shapes (polygons, polylines and points)
- .prj — projection format; contains the coordinate system and projection information
- .dbf — attribute format; contains attributes for each shape
Using the Shapefile Graph Generator
The Shapefile Graph Generator can read polygons and polylines from shapefiles. Polygons are imported as geographical regions while polylines can be processed to create different kinds of edges. If a shapefile contains a road network, the polylines could be used to create Road Transportation Edges.
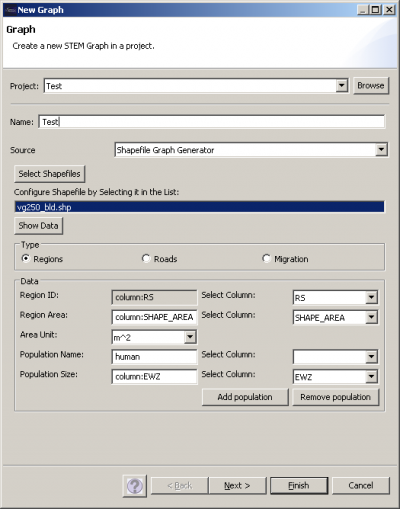
The UI for importing shapefiles can be displayed by choosing the item Shapefile Graph Generator in the New Graph wizard. Click on Select Shape Files to select multiple shapefiles in a file dialog. For each of the shapefiles, you must specify if the file contains regions, roads or polylines with migration data. Also you need to specify a unique ID for each shape by selecting an ID column in the related combo box. The data of all columns can be displayed by clicking on Show Data. For region shapefiles additional parameters can be specified (optional). These parameters are the Region Area, Area Unit (all areas are converted to km^2) and any number of populations (specified by Population Name and Population Size). If the shapefile contains roads or polylines with migration data, the following additional parameters must be specified: Road Class / Migration Population, Migration Rate. To do so, either use the data from a table column or enter the value for the parameter in the text field. In the latter case, the same value is used for all shapes.
Example 1
The shapefile used in this example can be downloaded from [1]. First the file vg250_bld.shp is loaded by clicking Select Shapefiles. The type is set to Regions, RS is used as Region ID, SHAPE_AREA as Region Area, m^2 as Area Unit. Then Add Population is clicked, Population Name is set to human and EWZ is used as Population Size.
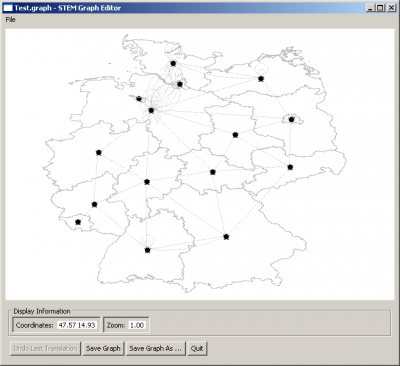
Running the Shapefile Graph Generator as shown above, the result should look like this in the Graph Editor.
Example 2
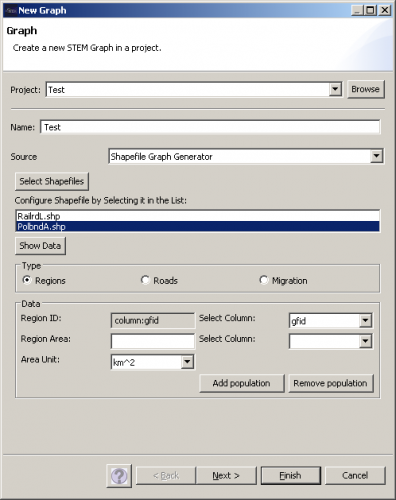
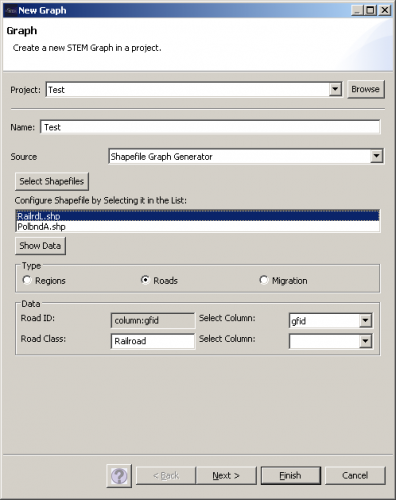
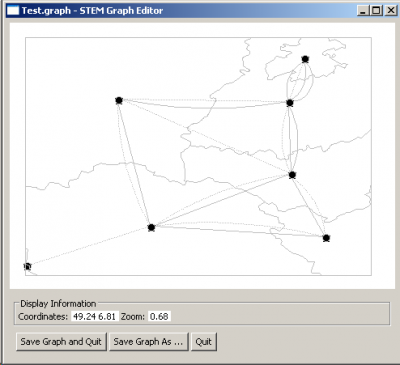
The shapefiles used in this example can be downloaded from [2]. The files PolbndA.shp and RailrdL.shp are loaded by clicking Select Shapefiles. First PolbndA.shp is selected, the type is set to Regions and gfid is used as Region ID. Then RailrdL.shp is selected, the type is set to Roads, gfid is used as Road ID and the Road Class is set to Railroad.
Running the Shapefile Graph Generator as shown above, the result should look like this in the Graph Editor.