Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
DD Manual Test Plan
Nav: DSDP/DD | DSDP/DD/Testing | DD Test Instructions | DD Known Issues and Workarounds | DD Manual Test Plan
Contents
DSF Features
Debug view
For the following tests, the PDA example debugger can be used with
Launching
- Debug perspective activation on launch
- Debug view activated on breakpoint hit
- Initial selection after launch
- If the program is suspended, top stack frame should be selected.
- If the program is running, the process should be selected.
Target/Launch/Processes
- Process label display
- Resume/suspend operations on process node
- All threads should resume/suspend
- Stepping operations should be disabled
- Terminating the target
- Terminated target should remain in the view with a "<terminated>" label prefix a terminated target icon. Alternatively, the target can simply be removed from the view.
- Check: The launch should also have a "<terminated>" prefix in the view.
- Running program to the completion,
- Target should change state to terminated
- The process (node representing the process) should also change state to terminated.
- If all processes are in terminated state, the launch should also be in terminated state.
Threads
- Thread label display
- Resume/suspend operations
- Step operations
- Multi-threaded program
- New threads should be added to the bottom of the thread list as they are created
- Exiting threads are removed from the thread list
- When stepping a thread, other threads should remain collapsed/expanded as they were
- Manual refresh mode
- New threads should not be added to the thread list, and old threads should remain.
- The refresh button in view should update the thread list.
Stack frames
- Check: frame label should contain:
- Stack frame number
- Function name if known
- File and line
- Current program counter
- Select a stack frame
- Check: source editor is opened and positioned to the location of the PC
- Check: run control operations should be the same as when a thread is selected
- Check: when a thread hits a breakpoint, that thread's stack frame is automatically selected
- Check: frame label should contain:
Source Display
- Run a program with multiple source files
- Set a breakpoint at a function call which is in another source file
- Run to breakpoint
- Check: the source file with the breakpoint is displayed
- Step into the function
- Check: the new source file is displayed at the start of the new function
Fast stepping
- Stepping fast by holding down the F5 key
- The Instruction Pointer in the editor should be painted after every step
- The line high-lighting selection in the editor should disappear until stepping slows down
- Minimum step interval preference
- Delay stepping to update views preference
Variables view
- Stop a debugged program when it has at least two stack levels
- Open variables view
- Check that all variables of the current stack are shown
- Check that all values are shown
- Check that the layout menu behaves as expected
- Check that complex variables have a little arrow on the left
- Check that the arrow can be expanded to show children
- Select different variables in the view and check that the details pane shows the different formats
- Scroll down in the variable view
- Check that newly displayed variables are correct
- Change the stack frame in the debug view
- Check that the variables view properly shows the variables for the selected stack frame
- Go back to the previous stack frame in the debug view
- Check that the variables view properly shows the variables for the selected stack frame
- Step the program
- Check that variable changes are reflected in the view and highlighted in color
- Select a variable and change its value in the variables view
- Check that the value is shown in the view
- Step the program
- Check that the value for the changed variable is still correct
Registers view
- Launch a C/C++ Local Application (Experimental - DSF) containing:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void level_04( int level )
{
printf( "yes we are\n" );
}
void level_03( int level )
{
printf( "yes we are\n" );
level_04( 4 );
}
void level_02( int level )
{
printf( "yes we are\n" );
level_03( 3 );
}
void level_01( int level )
{
printf( "yes we are\n" );
level_02( 2 );
}
int main(void) {
level_01( 1 );
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
- Step into until you are in the level_04() routine
- Bring up the register view ( leave all register groups unexpanded )
- Select between the various stack frames
- Check: The Register Groups remain unexpanded.
- Now select stack frame level_04() and then expand the first ( perhaps only ) group in the Register view
- Now select the level_03() stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Now select the level_02() stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Now select the level_01() stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Now select the main() stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Now select the Thread[1] entry.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Select the Launch entry for the current application
- Check: The Registers view redraws showing nothing
- Reselect the level_04() stack frame
- Stretch the Register View to insure that the eip and eflags registers are visible
- Perform a Step_over
- Check: The eip and eflags registers are highlighted as changed
- Check: The eip indicates we are still at level_04 somewhere
- Step until back at level_03()
- Check: The Registers View did not redraw
- Check: The General Registers group retained its expansion
- Check: The eip now indicates level_03 in it.
- Select the $eax register. Click in the "Value" field to begin cell editing.
- No matter what the current value, type in a 0x12
- Check: The new value of $eax is 0x12
- With the registers group expanded scroll to the bottom of the view
- Check: All registers update with what appear to be correct values
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Binary
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a BINARY form
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Octal
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a OCTALform
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Decimal
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a DECIMAL form
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Hex
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a HEX form
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Natural
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a NATURAL form
- Launch a DSF PDA Application containing ( this is the fibonacci.pda file ) :
push 6 call fibonacci output halt # # f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2) # f(0) = 1 # f(1) = 1 # :fibonacci var n pop $n push $n branch_not_zero gt0 push 1 return :gt0 push $n dec branch_not_zero gt1 push 1 return :gt1 push $n dec call fibonacci push $n dec dec call fibonacci add return
- Set a breakpoint at the "var n" line within the fibonacci function
- Hit the F8 key 6 times so there are 6 stack frames showing
- Bring up the register view ( leave all register groups unexpanded )
- Select between the various stack frames
- Check: The Register Groups remain unexpanded.
- Now select stack frame 6 and then expand the "General" group
- Now select and expand the "status" register within the "General" group
- Now select the level 5 stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Now select the level 5 stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Now select the level 4 stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Now select the level 3 stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Now select the level 2 stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Now select the level 1 stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- Select the Launch entry for the current application
- Check: The Registers view redraws showing nothing
- Reselect the level 6 stack frame
- Hit F8 until there are only 4 stack frames
- Check: The Registers View did not redraw
- Check: The General Registers group retained its expansion
- Select the $pc register. Click in the "Value" field to begin cell editing.
- Check: The regxister could not be edited ( it is read only )
- With the registers group expanded scroll to the bottom of the view
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Binary
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a BINARY form
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Octal
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a OCTALform
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Decimal
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a DECIMAL form
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Hex
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a HEX form
- Leave the registers group expanded - In the drop down menu tab select Number Format - Natural
- Check: All currently expanded/displayed registers change to display their values in a NATURAL form
Expressions view
- Stop a debugged program when it has at least two stack levels
- Open expressions view
- Create two or three expressions including some of children of variables
- Check that an expression can be added with the "Add new expression" line
- Check that an expression can be added with "Add Watch Expression" context menu
- Check that the created expressions are shown
- Check that expressions values are shown
- Check that the layout menu works as expected
- Check that complex expressions have a little arrow on the left
- Check that the arrow can be expanded to show children
- Select different expressions in the view and check that the details pane shows the different formats
- Add expressions to allow to scroll down in the expressions view
- Check that newly displayed expressions are correct
- Change the stack frame in the debug view
- Check that the expressions view properly shows the expressions for the selected stack frame
- Go back to the previous stack frame in the debug view
- Check that the expressions view properly shows the expressions for the selected stack frame
- Step the program
- Check that expressions changes are reflected in the view and highlighted in color
- Select a expressions and change its value in the expressions view
- Check that the value is shown in the view
- Step the program
- Check that the value for the changed expression is still correct
- Remove an expression using the context menu
- Check that the expression is removed
- Check that the same expression can be added again
- Check that expansion state is retained as expressions are added/removed.
- Remove all expressions using the context menu "Remove all..." command
- Check that all expressions are removed
- Check that expressions can be added again
- Modify an expression directly in the view
- Check that the expression changes and its value and type correspond to the new expression
Modules view
- Start a debug session and open the Modules view.
- Select the process in Debug view
- Check that the list of modules is shown in the Modules view.
- Select a thread then a stack frame in Debug view.
- Check that the Modules view still shows a list of loaded modules.
- Select a module in the modules view.
- Check that the detailed module info (type, symbols loaded, file, base address, size) are shown.
Number formats detail pane
- Launch a C/C++ Local Application (Experimental - DSF) containing:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void level_04( int level )
{
printf( "yes we are\n" );
}
void level_03( int level )
{
printf( "yes we are\n" );
level_04( 4 );
}
void level_02( int level )
{
printf( "yes we are\n" );
level_03( 3 );
}
void level_01( int level )
{
printf( "yes we are\n" );
level_02( 2 );
}
int main(void) {
level_01( 1 );
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
puts("Are we having fun yet"); /* prints Are we having fun yet */
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
- Step into until you are in the level_04() routine
- Bring up the register view and expand the General Registers group.
- Now select the level_04() stack frame.
- Check: See that the expanded group retains its expansion.
- In the Register View select the $eax register.
- Check: Examine the Details Pane and see that the pane reflect the current value in all supported modes.
- Select the $eax register for editing and change its value to 0.
- Check: Examine the Details Pane and see that the pane shows all 0's for the various values.
- Select the $eax register for editing and change its value to 1.
- Check: Examine the Details Pane and see that the pane shows all 1's for the various values.
- Select the $eax register and then additionally select the $ebx register
- Check: Examine the Details Pane and see both registers are represented there.
- In the Register View select the $eax register.
- In the Details Pane select anything and right mouse click and perform "Select All"
- Check: Examine the Details Pane and see that all of the text representing the $eax register is selected.
- Right mouse Click and perform Copy, bring up a separate editor and perform a paste.
- Check: The fully highlighted text is correctly pasted into the editor.
- In the Registers View select some register which is typically now 0 ( contains a real/large value)
- Slide the left side of the register view over until the details pane redraws to try and fit the text.
- Select in the details pane and click "Wrap Text" to turn it off.
- Check: See that the text is not longer wrapped and disappears off the screen.
- Select in the details pane and click "Wrap Text" to turn it on.
- Check: See that the text is not longer is now wrapped to try and be visible on the screen.
- Select in the details pane and click "Max Length"
- Change the length to 4 and select OK.
- Reselect the $eax register.The Detail Pane now just shows "Name..."
- Select in the details pane and click "Max Length"
- Change the length to 500 and select OK.
- Reselect the $eax register.The Detail Pane correctly shows all of the supported formats.
Update modes
- (Perform tests using one of: Variables, or Registers, or Expressions view)
- Selecting a mode
- Before launching a program.
- Check: Update Modes menu is disabled.
- Start a program.
- Check: Update Modes menu is enabled.
- Select Manual Mode
- Check: Open the menu again and confirm that the Manual mode is selected.
- Terminate the program and relaunch
- Check: Confirm that the Manual mode is selected still.
- Terminate the Eclipse workbench and restart it, relaunch the program.
- Check: Confirm that the Manual mode is selected still.
- In another view, select the "Breakpoint Hit" mode.
- Check: In the first view, confirm that the Manual mode is still selected.
- Automatic mode
- Launch a program and select the automatic mode in the view.
- Step through the program .
- Check: Confirm that variables/registers ARE updated with every step.
- Run to a breakpoint.
- Check: Confirm that variables/registers ARE updated.
- Manual mode
- Select the Manual mode.
- Step through the code.
- Check: Verify that variables/registers ARE NOT updated.
- Run to a breakpoint.
- Check: Confirm that variables/registers ARE NOT updated.
- Breakpoint hit mode
- (Using one of: Variables, or Registers, or Expressions view)
- Select the Breakpoint hit mode
- Step through the code
- Check: Verify that variables/registers ARE NOT updated.
- Run to a breakpoint.
- Check: Confirm that variables/registers ARE updated.
- Refresh Action
- Select Manual update mode.
- Step through code
- Select the Refresh action.
- Check: Verify that variables/registers are updated and that changed values are highlighted.
- Select the Refresh action again.
- Check: Verify that variables/registers remain unchanged and that highlighted values are no longer highlighted.
- "Debug Update Modes" action set
- Update Policy, Refresh, Refresh All actions should only appear in view if the action set is active.
- Refresh All
Breakpoints (General)
Before you start...
- To avoid stack overflow, set memory to 512M
- In the launch configuration, Arguments tab, VM arguments section: -Xmx512M
- To ensure integrity between the UI and the back-end, all verifications (Check:) are performed from 3 points:
- Back-end activities with GDB/MI traces
- Back-end breakpoint status with "info break" at the console
- Platform breakpoint status in Breakpoint View (with Breakpoint Properties)
Breakpoints
- Test Setup
- Launch the Eclipse workbench
- Start a DSF debug session (DsfBreakpoints)
- Test 1: Breakpoint setting
- In the editor, add a new line breakpoint (BP-1)
- Check: A new breakpoint is inserted and it is enabled
- In the view menu: enable the "Show Full Paths" check box
- Check: The breakpoint full path is displayed in the view
- In the editor, disable the "Show Full Paths" check box
- Check: The breakpoint full path is not displayed in the view
- Test 2: Breakpoint activation
- Test 3: Breakpoint condition
- Set an invalid condition on BP-1
- Check: The update is rejected and BP-1 is not changed
- Set a valid condition on BP-1
- Check: The update is accepted and BP-1 has the new condition
- Set an invalid condition on BP-1
- Check: The update is rejected and BP-1 kept the valid condition
- Clear the BP-1 condition
- Check: The update is accepted and BP-1 no longer has a condition
- Test 4: Breakpoint ignore count
- Test 5: Breakpoint deletion (simple)
- From the GUI, delete BP-1
- Check: BP-1 is removed
- Test 6: Breakpoint persistence
- Create 4 breakpoints with the following characteristics:
- BP-1: enabled, no condition, no ignore count
- BP-2: disabled, with condition, no ignore count
- BP-3: disabled, no condition, with ignore count
- BP-4: enabled, with condition, with ignore count
- Check: The 4 breakpoints are correctly created
- Terminate the debugging session
- Start a new debugging session
- Check: The 4 breakpoints are correctly restored
- Terminate the debugging session
- Enable all breakpoints
- Start a new debugging session
- Check: The 4 breakpoints are correctly restored (and enabled)
- Create 4 breakpoints with the following characteristics:
- Test 7: Import/export breakpoints to file
- Create 4 breakpoints with the following characteristics (re-use the ones from previous step):
- BP-1: enabled, no condition, no ignore count
- BP-2: disabled, with condition, no ignore count
- BP-3: disabled, no condition, with ignore count
- BP-4: enabled, with condition, with ignore count
- Check: The 4 breakpoints are correctly created
- Export the 4 breakpoints to file
- Check: The breakpoints file is created
- Remove all breakpoints
- Check: The 4 breakpoints are removed
- Import the breakpoint file
- Check: The 4 breakpoints are correctly restored
- Remove all breakpoints
- Terminate the debugging session
- Start a new debugging session
- Check: No breakpoint is installed
- Import the breakpoint file
- Check: The 4 breakpoints are correctly restored
- Create 4 breakpoints with the following characteristics (re-use the ones from previous step):
- Test 8: Breakpoint deletion (multiple)
- From the GUI, delete BP-1, BP-2, BP-3 and BP-4
- Check: the 4 breakpoints are removed
Watchpoints
- Test Setup
- Launch the Eclipse workbench
- Start a DSF debug session (DsfBreakpoints)
- Test 1: Watchpoint setting
- In the Breakpoint View, add a new watchpoint (WP-1)
- Check: A new watchpoint is inserted and it is enabled
- Test 2: Watchpoint activation
- Test 3: Watchpoint condition
- Set an invalid condition on WP-1
- Check: The update is rejected and WP-1 is not changed
- Set a valid condition on WP-1
- Check: The update is accepted and WP-1 has the new condition
- Set an invalid condition on WP-1
- Check: The update is rejected and WP-1 kept the valid condition
- Clear the WP-1 condition
- Check: The update is accepted and WP-1 no longer has a condition
- Test 4: Watchpoint ignore count
- Test 5: Watchpoint deletion (simple)
- From the GUI, delete WP-1
- Check: WP-1 is removed
- Test 6: Watchpoint persistence
- Create 4 watchpoints with the following characteristics:
- WP-1 enabled, write, no condition, no ignore count
- WP-2 disabled, read, with condition, no ignore count
- WP-3 disabled, read/write, no condition, with ignore count
- WP-4 enabled, write, with condition, with ignore count
- Check: The 4 watchpoints are correctly created
- Terminate the debugging session
- Start a new debugging session
- Check: The 4 watchpoints are correctly restored
- Terminate the debugging session
- Enable all watchpoints
- Start a new debugging session
- Check: The 4 watchpoints are correctly restored (and enabled)
- Create 4 watchpoints with the following characteristics:
- Test 7: Import/export watchpoints to file
- Create 4 watchpoints with the following characteristics (re-use watchpoints from previous step):
- WP-1 enabled, write, no condition, no ignore count
- WP-2 disabled, read, with condition, no ignore count
- WP-3 disabled, read/write, no condition, with ignore count
- WP-4 enabled, write, with condition, with ignore count
- Check: The 4 watchpoints are correctly created
- Export the 4 watchpoints to file
- Check: The watchpoints file is created
- Remove all watchpoints
- Check: The 4 watchpoints are removed
- Import the watchpoints file
- Check: The 4 watchpoints are correctly restored
- Remove all watchpoints
- Terminate the debugging session
- Start a new debugging session
- Check: No watchpoints is installed
- Import the watchpoints file
- Check: The 4 watchpoints are correctly restored
- Create 4 watchpoints with the following characteristics (re-use watchpoints from previous step):
- Test 8: Watchpoint deletion (multiple)
- From the GUI, delete WP-1, WP-2, WP-3 and WP-4
- Check: The 4 watchpoints are removed
Skip All Button
- Test Setup
- Launch the Eclipse workbench
- Create 3 line breakpoints (anything will do)
- Start a DSF debug session (DsfBreakpoints)
- Check: Breakpoints are created and enabled
- Test 1: Simple ON/OFF
- Test 2: ON/OFF with some disabled BPs
- Disable BP 2
- Check: Only BP-2 is disabled
- Toggle the SAB to ON
- Check: All breakpoints are disabled
- Toggle the SAB to OFF
- Check: BPs 1, 3 are enabled
- Disable BP 1 and 3
- Enable BP 2
- Check: Only BP-2 is enabled
- Toggle the SAB to ON
- Check: All breakpoints are disabled
- Toggle the SAB to OFF
- Check: Only BP-2 is enabled
- Test 3: ON/OFF with all BPs disabled
- Test 4: Change BPs state while OFF
- Test 6: Startup
GDB Features
GDB Basic Sanity Test
- Check out and build the sanity test project from /cvsroot/dsdp/org.eclipse.dd.dsf/tests/SanityTest
- Launch the DSF debugger with break at main
- Follow instructions in the test.
Launching
- Perspective
- In Preferences->Run/Debug->Perspectives, make sure that at least one perspective change option is set to prompt.
- Set the java or c++ perspective
- Launch a DSF program
- Verify that there is a prompt to switch perspective to Debug, Answer yes
- Verify the perspective switches
- Expanding after launch
- Verify from the above test that the Debug view has a selection to the top-most thread
- Close Debug view
- Open Debug view
- Verify that the Debug view has a selection to the top-most thread
- Break on main
- Set a valid break-on-main symbol, and launch.
- Check: the program breaks at the correct location.
- Set an invalid break-on-main symbol, and launch.
- Check: the launch should fail with an error from creating the break-on-main breakpoint
- Set a break-on-main symbol that is not reachable by the program, but the program continues running, and launch.
- Check: the launch should complete as if there was no break-on-main symbol set.
- Set a break-on-main symbol that is not reachable by the program, but and the program exits quickly.
- Check: the launch should complete and the program should run and terminate normally.
- Remote Launch
- Start a gdbserver session with the binary of the eclipse C++ project
- Use the DSF Remote launch to connect to that gdbserver
- Verify that the debugging session is the same as a local debugging session
- Verify that the Restart button is grayed out
- Local Attach Launch
- Start the binary of your project outside of eclipse (this binary should take a long time to execute to give you enough time to attach to it)
- Use the DSF Attach to Local applicaiton launch
- Verify that a popup window prompts for the process to attach to
- Select the binary you started
- Verify that the debugging session is the same as a local debugging session
- Verify that the Restart button is grayed out
- Verify that the output of the binary remains on the terminal where it was started
- Remote Attach Launch
- Start a gdbserver session with the --multi flag and no binary
- Start the binary of your project outside of eclipse (this binary should take a long time to execute to give you enough time to attach to it)
- Use the DSF Attach launch to connect to that gdbserver using the 'gdbserver Debugger' type
- Verify that a popup window prompts for the process pid to attach to (no list)
- Put in the pid of the binary you started
- Verify that the debugging session is the same as a local debugging session
- Verify that the Restart button is grayed out
- Verify that the output of the binary remains on the terminal where it was started
- Output
- Launch a local debug session
- Step the program to execute a couple of instructions that have a printf
- Verify that the output of the program is properly seen in a separate console.
- Restart
- Launch a local debug session
- Step the program to execute a couple of instructions
- Press the Restart button and verify that the program restarts from the beginning
- Verify also that the "Break on main option is still respected on the restart
- Verify also that the output of the program is properly seen in a separate console.
Breakpoints (CDT)
Before you start...
- To avoid stack overflow, set memory to 512M
- In the launch configuration, Arguments tab, VM arguments section: -Xmx512M
- To ensure integrity between the UI and the back-end, all verifications (Check:) are performed from 3 points:
- Back-end activities with GDB/MI traces
- Back-end breakpoint status with "info break" at the console
- Platform breakpoint status in Breakpoint View (with Breakpoint Properties)
Thread Filters
- Test Setup
- Test 1: Filter out a thread
- Test 2: Filtered thread substitution
- Test 3: Remove a filtered thread
- Test 4: Add a filtered thread
- Change filter for thread 2, 3
- Check: 2 identical breakpoints are installed, one for each thread selected
- Test 5: Remove thread filters
- Test 6: Initial state propagation
- Test 7: Invalid condition propagation
- Test 8: Valid condition propagation
- Add a valid condition
- Check: Condition is properly set for both breakpoints
- Test 9: Condition/Ignore count removal propagation
- Remove condition and ignore count
- Check: Condition and ignore count are removed from both breakpoints
- Test 10: State persistence
- Test 11: Simultaneous update of state and thread filter
- Add filter for threads 1, 2, a valid condition and an ignore count
- Check: The original breakpoint is removed
- Check: 2 new breakpoints are set with proper ignore count, condition
- Remove thread filter
- Check: The breakpoints for threads 1, 2 are removed
- Check: A new breakpoint is set with the correct condition, ignore count and no thread filter
- Test 12: Addition of thread filter, invalid condition and ignore count
- Add filter for threads 1, 2, invalid condition, ignore count
- Check: The original breakpoint is removed
- Check: 2 new breakpoints are set with proper ignore count and old (valid) condition
- Remove thread filter
- Check: The breakpoints for threads 1, 2 are removed
- Check: A new breakpoint is set with the correct condition, ignore count and no thread filter
- Test 13: Enable, disable breakpoints
- Disable the breakpoint
- Check: The breakpoint is disabled
- Add filter for threads 1, 2
- Check: The original breakpoint is removed
- Check: 2 new disabled breakpoints are set with proper ignore count, condition
- Enable the breakpoint
- Check: Both back-end breakpoints are enabled
- Remove thread filter
- Check: The breakpoints for threads 1, 2 are removed
- Check: A new (enabled) breakpoint is set with the correct condition, ignore count and no thread filter
Memory Components
Traditional Memory Rendering
- Launch a debug session against an application containing:
int main(void) {
int i = 0;
int j = 10;
int k = 20;
while(1) {
i++;
j++;
k++;
printf("i: %d, j: %d, k: %d\n", i, j, k);
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
- Step past "i = 0"
- In the Memory View, create a new memory monitor at address "&i"
- Create a new Traditional Rendering
- Check: Rendering components paints without generating entries in the Errors view
- Scroll the view
- Check: Rendering repaints with adequate performance
- Edit memory at &i
- Check: Edited memory paints in edit color
- Press enter to submit changed value
- Check: Changed memory paints in history color
- Step multiple times, on each step checking:
- Check: history coloring
- Select some memory
- Check: selection paints properly
- Context menu -> Copy to Clipboard
- Check: paste clipboard contents in an editor window; contents should match previously selected memory
- Content menu -> Copy Address
- Check: clipboard contents should be the address of the data at the context click
- Context menu -> Endian
- Check: correct default value based on target connection
- Try each: Context -> Panes, Endian, Text, Cell Size, Radix, Columns
- Check: repaint, correct setting applied
- Window -> Preferences -> Run/Debug -> Traditional Memory Rendering; change all preferences
- Check: verify preferences have applied
Import/Export
- continuing with above debug session:
- Toolbar -> Export -> SRecord, set a valid range and file
- Check: contents of file match data in view
- Toolbar -> Export -> Plain Text, set a valid range and file
- Check: contents of file match data in view
- Toolbar -> Import -> SRecord, import previously exported file to a different location
- Check: contents in view match file
- Toolbar -> Import -> Plain Text import previously exported file to a different location
- Check: contents in view match file
Find/Replace
- continuing with above debug session:
- Action menu -> Find/Replace
- for each available format, with start and end set 1000 within the viewport start and end, search for data known to be within the current viewport
- Check: view scrolls to found data
- for each available format, with start and end set 1000 within the viewport start and end, search for data known to not be within the current viewport, but withiin the specified range
- Check: view scrolls to found data
- for each available format, with start and end set 1000 within the viewport start and end, search for data known to not be within the specified range
- Check: view indicates "not found" status
- perform an ascii search, case insensitive, for tEd where only TeD is within the specified memory range
- Check: view scrolls to found data
- perform an ascii search with wrap search enabled, where matching string is only above the viewport
- Check: view scrolls to found data
- perform a hex search with "backward" selected with matching values before and after the viewport start address.
- Check: view scrolls in correct direction
- perform an ascii search with start 0, end FFFFFFFF, for a string known to not exist in said memory. cancel the job from the progress view.
- Check: search terminates.
IP-XACT Editor
More tests to be added
The following tests are intended to be run sequentially, and later tests depend on things set up in earlier tests.
- Test 1 - GUI additions
- Launch Eclipse with IP-XACT editor installed, and an empty workspace.
- Open or select the Resource perspective.
- Select Window/Open perspective/Other..
- Check: that the IP-XACT perspective is in the list shown in the dialog box
- Press cancel
- Select File/New/Other...
- Check: that the dialog box contains an entry for IP-XACT, and when this is expanded it contains an entry for IP-XACT file
- Press cancel
- Select Window/Preferences...
- Check: that the left hand side of the dialog box contains an entry for IP-XACT
- Click on this entry
- Check: that the IP-XACT preferences window appears and contains two modifiable fields: 'Default Vendor Name' and 'Default Library Name'
- Expand the IP-XACT menu item in the left subwindow.
- Check: that it has a sub-entry for 'Document Checker'
- Click on 'Document Checker' in the left subwindow.
- Check: that the Document Checker preferences window appears and contains:
- A 'File Paths Variables' table, with two columns; 'Variable' and 'Value'
- New, Remove, and Edit buttons associated with this table.
- A 'Treat System Variables as File Path Variables' check box associated with this table
- A 'File Paths Roots' table
- New, Remove, Up, and Down buttons associated with this table.
- Press cancel
- Test 2 - IP-XACT perspective
- Open the IP-XACT perspective
- Reset the perspective (Window/Reset Perspective)
- Check: The perspective contains the views shown in the attached image, arranged this way (possibly scaled for Eclipse window size etc.)
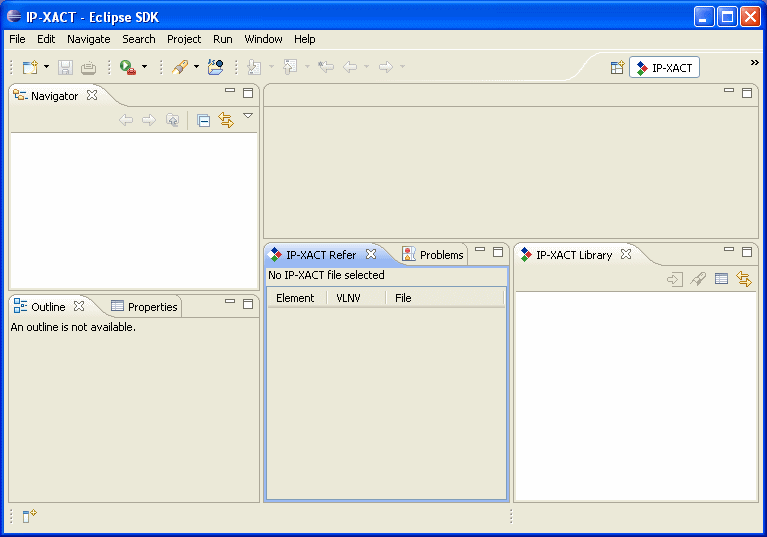
- Check: The IP-XACT icon on the IP-XACT views matches that shown in the image.
- Create a new project with New/Project.../General/Project
- Name the project 'Test'
- In the navigator window right click on the test project and select 'New'
- Check: 'IP-XACT file...' appears in the submenu
- Test 3 - Creating IP-XACT files.
- Right click on 'Test' in the Navigator window
- Select New/IP-XACT file...'
- Check: A wizard starts with title 'Create IP-XACT file'
- Check: The first page of the wizard is file creation dialog with title 'IP-XACT file name', default folder 'Test' and default name 'NewFile.spirit'
- Click 'Next'
- Check: The second page of the wizard has title Select IP-XACT schema standard and a pull down giving the option of 'IP-XACT Standard V1.4' or 'IP-XACT Standard V1.2'
- Select 'IP-XACT Standard V1.4' and click 'Next'
- Note: there may be a slight delay before the next page appears.
- Check: The third page of the wizard appears as shown below:
- Check: The pull-down menu contains the items:
- abstractionDefinition
- abstractor
- busDefinition
- component
- design
- designConfiguration
- generatorChain
- Select 'abstractionDefinition' on the pull-down menu, and leave everything else unchanged. Click Next
- Check: The fourth page of the wizard appears title 'Set VLNV' and four settable fields:
- Vendor - initialized to <username>
- Library - initialized to <username>Lib
- Name - initialized to NewFile
- Version - initialized to 1.0
- Change the Vendor to 'example.org', and the Library to 'Test'
- Click Finish
- Check:
- NewFile.spirit appears under Test in the Navigator window, with an IP-XACT icon
- The IP-XACT editor (with an IP-XACT icon) opens for NewFile.spirit.
- An outline of NewFile.spirit appears in the outline window
- A new entry appears for example.org in the IP-XACT library window
- Select the Source tab at the bottom of the editor (if not already selected).
- Check: The following XML should be visible in the editor.
- Check: The pull-down menu contains the items:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <spirit:abstractionDefinition xmlns:spirit="http://www.spiritconsortium.org/XMLSchema/SPIRIT/1.4" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.spiritconsortium.org/XMLSchema/SPIRIT/1.4 http://www.spiritconsortium.org/XMLSchema/SPIRIT/1.4/index.xsd "> <spirit:vendor>example.org</spirit:vendor> <spirit:library>Test</spirit:library> <spirit:name>NewFile</spirit:name> <spirit:version>1.0</spirit:version> <spirit:busType spirit:library="Name" spirit:name="NMTOKEN" spirit:vendor="Name" spirit:version="NMTOKEN"/> <spirit:ports> <spirit:port> <spirit:logicalName>Name</spirit:logicalName> <spirit:wire/> </spirit:port> </spirit:ports> </spirit:abstractionDefinition>
- Test 4 - Text Editing features
- Note: This is only a basic sanity check for these features, since the IP-XACT editor is reusing the existing XML editor, and these features should be fully tested by the developers of the XML editor (or of the text editor from which it is derived).
- In the Test project make a copy of NewFile.spirit, called 'Copy of NewFile.spirit'
- Double click on 'Copy of NewFile.spirit' to open the IP-XACT editor.
- Select the source tab in the editor (if not already selected)
- Check: Type some text into the editor and check that it appears in the window.
- Check: that you can copy and paste the text correctly using either menu options or keyboard shortcuts.
- Check: that searches (ctrl/F) work correctly, with and without replacement.
- Save the file.
- Close the editor.
- Reopen the editor.
- Check: Your changes have been preserved.
- Delete 'Copy of NewFile.spirit'
- Test 5 - XML Editing features
- Note: This is only a basic sanity check for these features, since the IP-XACT editor is reusing the existing XML editor, and these features should be fully tested by the developers of the XML editor.
- Copy NewFile.spirit to 'Copy of NewFile.spirit'
- Double click on 'Copy of NewFile.spirit' to open the IP-XACT editor.
- Select the Design tab in the editor
- Right click on "abstractionDefinition"
- Open the Add Child sub-menu
- Check: This menu should contain:
- description
- extends
- vendorExtensions
- Comment
- Add Processing Instruction
- Select 'description'
- Check: a new 'spirit:description' entry appears as the last line of the table
- Select the second (value) field of this table entry and type 'A description', replacing the existing text.
- Expand the 'spirit:ports' table entry
- Expand the 'spirit:port' table entry
- Right click on 'spirit:wire'
- Check: The menu that appears should contain 'Replace with'
- Select 'Add child'
- Select 'onMaster'
- Right click on 'spirit:onMaster'
- Select 'Add child' and 'direction'
- Click on the right hand value field of the new 'spirit:direction' row
- [[Check:] A pull down menu appears giving the possible value 'in','out', and 'inout'
- Select 'in'.
- Select the 'Source' tab
- Reformat the source using Ctrl/Shift/F
- Check: The editor window should now contain the following XML.
- Note: The format may vary, only the content is important.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <spirit:abstractionDefinition xmlns:spirit="http://www.spiritconsortium.org/XMLSchema/SPIRIT/1.4" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.spiritconsortium.org/XMLSchema/SPIRIT/1.4 http://www.spiritconsortium.org/XMLSchema/SPIRIT/1.4/index.xsd "> <spirit:vendor>example.org</spirit:vendor> <spirit:library>Test</spirit:library> <spirit:name>NewFile</spirit:name> <spirit:version>1.0</spirit:version> <spirit:busType spirit:library="Name" spirit:name="NMTOKEN" spirit:vendor="Name" spirit:version="NMTOKEN" /> <spirit:ports> <spirit:port> <spirit:logicalName>Name</spirit:logicalName> <spirit:wire> <spirit:onMaster> <spirit:direction>in</spirit:direction> </spirit:onMaster> </spirit:wire> </spirit:port> </spirit:ports> <spirit:description>A description</spirit:description> </spirit:abstractionDefinition>
