|
A powerful feature of the Aggregator is the ability to create aggregated repos that can be consumed as Maven repos, (i.e. providing the directory/file structure and artifacts required by Maven). An aggregated repository that supports Maven can be consumed both as a p2 and a Maven repo (at the same time). This flexibility is possible thanks to p2's separation of dependency meta-data and the actual location of the referenced artifacts.
In order to create a Maven-conformant aggregate repo all that is required is to set the property Maven Result property of the Aggregation to true. The aggregation deployed to the Build Root location will be a Maven repo. In this repo all .source artifacts will be co-located with their main artifact, sharing the same artifactId but with qualifier -sources, as expected by Maven.
Additionally, the property Version Format of the Aggregation allows to select between three strategies for version numbers:
- Normal
- Versions numbers are kept unmodified
- Strict Maven
- Use a '-' (dash) to separate three-part versions from any qualifier, to make the resulting versions parsable by Maven (so 3.12.2.v20161117-1814 will be converted to 3.12.2-v20161117-1814).
- In previous versions this strategy was selected via property Strict Maven Versions which is now deprecated in favor of Version Format.
- Maven Release
- Cut off any qualifier, i.e., produce three-part version numbers to tell Maven that all artifacts are "releases".
If more fine grained control over version formats is needed, each Maven Mapping can be fine tuned with a pair of Version Pattern and Version Template, which will only be applied to artifacts matching the corresponding Maven Mapping. In this case, the existing version will be matched against the pattern, and if it matches, the version will be replaced by applying the corresponding template, where $1, $2 ... represent match groups from the pattern. As an example consider the case where the micro digit of a version should be omitted if it is equal to '0', so "4.12.0.v201504281640" will be translated to "4.12":
- Version Pattern: ([^.]+)\.([^.]+)\.0(?:\..*)?
- Version Template: $1.$2
Maven Snapshots
Using the final solution from bug 406557 (available since build I20200625-1232) it is possible to produce artifacts that maven recognizes as snapshots. The solution consists of several parts:
- Individual Maven Mapping elements can be marked with
snapshot="true". Aggregator will attempt to transform all matched artifacts to snapshot artifacts.
- The internal version identifying an individual snapshot in maven (smth like "1.2.3-20201253.235900-123") will be constructed from the following:
- Date and time will be extracted from the qualifier part of the OSGi version
- A build number needs to be passed as a command line argument to the aggregator like this:
--mavenBuildNumber 123. Build numbers should monotonically grow, but now further constraints apply.
The OSGi version qualifier (like "v20201224-2359-nightly") will be matched against the following pattern: "(.*[^0-9])?(\\d\\d\\d\\d\\d\\d\\d\\d)-?(\\d\\d\\d\\d(\\d\\d)?).*"
- an optional prefix ending in a non-digit will be ignored ("v")
- next 8 chars must be digits interpreted as the date ("20201231")
- an optional
"-" separator will be skipped ("-")
- next, 4 or 6 digits are expected, interpreted as the time (if only 4 digits they will be right-padded) ("235900")
- arbitrary postfix is again ignored ("nightly")
Version qualifiers not matching that pattern cannot be used for creating a maven snapshot.
By marking individual Maven Mappings as snapshot it is possible to create snapshot artifacts which then depend on release versions of other artifacts.
Example
A sample aggr file, SDK4Mvn.aggr, shows an easy-to-use example of how to create a Maven-conformant p2 repository (i.e. one that works with Maven or p2). The sample has a short description file that explains some of the details.
Headless support
You will need a headless installation of CBI with the Aggregator feature installed.
Running from the command line
Just type:cbiAggr aggregate <options>
Note: if you install the aggregator into an Eclipse SDK or Platform (rather than a pure headless installation), you can run from the command line, by using
eclipse -application org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.cli.headless aggregate <options>
For a detailed listing of the available options consult the next section.
Command line options
| Option
|
Value
|
Default
|
Description
|
| --buildModel
|
<path to build model>
|
This value is required
|
Appoints the aggregation definition that drives the execution. The value must be a valid path to a file (absolute or relative to current directory).
|
| --action
|
VALIDATE (VERIFY in 0.1)
BUILD
CLEAN
CLEAN_BUILD
|
BUILD
|
Specifies the type of the execution.
- VALIDATE - verifies model validity and resolves dependencies; no artifacts are copied or created
- BUILD - performs the aggregation and creates the aggregated repository in the target location
- CLEAN - cleans all traces of previous aggregations in the specified target location
- CLEAN_BUILD - performs a CLEAN followed by a BUILD
|
| --buildId
|
<string>
|
build-<timestamp in the format yyyyMMddHHmm>
|
Assigns a build identifier to the aggregation. The identifier is used to identify the build in notification emails. Defaults to: build-<timestamp> where <timestamp> is formatted according as yyyyMMddHHmm, i.e. build-200911031527
|
| --buildRoot
|
<path to directory>
|
buildRoot declared in the aggregation model
|
Controls the output. Defaults to the build root defined in the aggregation definition. The value must be a valid path to a directory (absolute or relative to current folder). If the desired directory structure does not exist then it is created.
|
| --agentLocation
|
<path to directory>
|
<buildRoot>/p2
|
Controls the location of the p2 agent. When specified as outside of the build root, the agent will not be cleaned out by the aggregator and thus retain its cache.
|
| --production
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Indicates that the build is running in real production. That means that no mock emails will be sent. Instead, the contacts listed for each contribution will get emails when things go wrong.
CAUTION: Use this option only if you are absolutely sure that you know what you are doing, especially when using models "borrowed" from other production builds without changing the emails first.
|
| --emailFrom
|
<email>
|
Address of build master
|
Becomes the sender of the emails sent from the aggregator.
|
| --emailFromName
|
<name>
|
If --emailFrom is set then this option sets the real name of the email sender.
|
| --mockEmailTo
|
<email>
|
no value
|
Becomes the receiver of the mock-emails sent from the aggregator. If not set, no mock emails are sent.
|
| --mockEmailCC
|
<email>
|
no value
|
Becomes the CC receiver of the mock-emails sent from the aggregator. If not set, no mock CC address is used.
|
| --logURL
|
<url>
|
N/A
|
The URL that will be pasted into the emails. Should normally point to the a public URL for output log for the aggregator so that the receiver can browse the log for details on failures.
|
| --logLevel
|
DEBUG
INFO
WARNING
ERROR
|
INFO
|
Controls the verbosity of the console trace output. Defaults to global settings.
|
| --eclipseLogLevel
|
DEBUG
INFO
WARNING
ERROR
|
INFO
|
Controls the verbosity of the eclipse log trace output. Defaults to global settings.
|
| --stacktrace
|
---
|
no value
|
Display stack trace on uncaught error.
|
| --subjectPrefix
|
<string>
|
?
|
The prefix to use for the subject when sending emails. Defaults to the label defined in the aggregation definition. The subject is formatted as: "[<subjectPrefix>] Failed for build <buildId>"
|
| --smtpHost
|
<host name>
|
localhost
|
The SMTP host to talk to when sending emails. Defaults to "localhost".
|
| --smtpPort
|
<port number>
|
25
|
The SMTP port number to use when talking to the SMTP host. Default is 25.
|
| --packedStrategy
|
COPY
VERIFY
UNPACK_AS_SIBLING
UNPACK
SKIP
|
value from the model
|
Deprecated (Use only with on-the-fly transformation from deprecated build models)
Controls how mirroring is done of packed artifacts found in the source repository. Defaults to the setting in the aggregation definition.
|
| --trustedContributions
|
<comma separated list>
|
no value
|
Deprecated (Use only with on-the-fly transformation from deprecated build models)
A comma separated list of contributions with repositories that will be referenced directly (through a composite repository) rather than mirrored into the final repository (even if the repository is set to mirror artifacts by default).
Note: this option is mutually exclusive with option --mavenResult (see below)
|
| --validationContributions
|
<comma separated list>
|
no value
|
Deprecated (Use only with on-the-fly transformation from deprecated build models)
A comma separated list of contributions with repositories that will be used for aggregation validation only rather than mirrored or referenced into the final repository.
|
| --mavenResult
|
---
|
no value
|
Deprecated (Use only with on-the-fly transformation from deprecated build models)
Tells the aggregator to generate a hybrid repository that is compatible with p2 and maven2.
Note: this option is mutually exclusive with option --trustedContributions (see above)
|
| --mirrorReferences
|
---
|
no value
|
Mirror meta-data repository references from the contributed repositories. Note the current recommendation is to not have update sites in feature definitions, but instead in "products", that is, to allow adopters or consumers to specify where to get updates from and what "extras" to offer. See bug 358415. But, this option can still useful for some situations.
|
| --referenceIncludePattern
|
<regexp>
|
no value
|
Include only those references that matches the given regular expression pattern.
|
| --referenceExcludePattern
|
<regexp>
|
no value
|
Exclude all references that matches the given regular expression pattern. An exclusion takes precedence over an inclusion in case both patterns match a reference.
|
| --mavenBuildNumber
|
<number>
|
no value
|
When producing a maven snapshot the build number is supposed to uniquely identify a particular snapshot build.
|
Aggregation model components and specific actions
This section provides an in-depth description and reference of the Aggregation model, listing all model components, properties and available actions.
Global actions
The following aggregator-specific actions are available via the context menu that can be invoked on any node in the Aggregation model editor:
- Clean Aggregation - cleans all traces of previous aggregations in the specified target location (Build Root)
- Validate Aggregation - verifies model validity and resolves dependencies; no artifacts are copied or created
- Build Aggregation - performs the aggregation and creates the aggregated repository in the target location (Build Root)
- Clean then Build Aggregation - performs a Clean followed by a Build
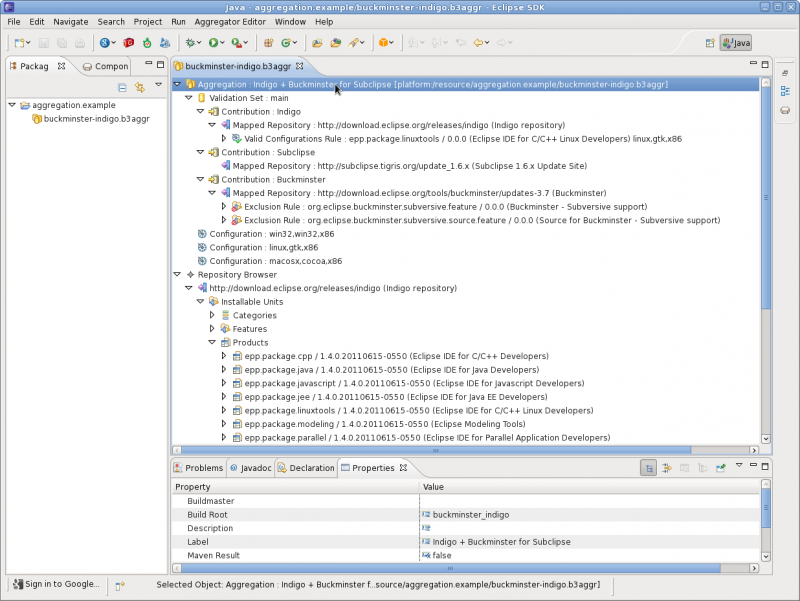
Aggregation
The root node of any aggregation model is the Aggregation node. It specifies a number of global properties including the Build Root (the target location of the aggregated repository) as well as the repo structure (maven-conformant or classic p2 setup).
There are several child components some of which can be reference in other parts of the model: Configuration, Contact,Validation Set, Custom Category, Maven Mapping.
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Buildmaster
|
<Contact>?
|
-
|
Specifies an optional build master that will be notified of progress and problems if sending of mail is enabled. This is a reference to any Contact that has been added to this Aggregation model.
|
| Build Root
|
<urn>
|
-
|
This is a required property specifying the target location of the aggregated repository.
|
| Description
|
<string>
|
-
|
An optional description of the aggregated repository that will be shown when accessing the aggregated repository via the p2 update manager.
|
| Label
|
<string>
|
-
|
A required label that will be used for the aggregated repository. This will be shown as the repo label when accessing the aggregated repository via the p2 update manager.
|
| Maven Mappings
|
<Maven Mapping>*
|
-
|
References Maven Mappings added as children to the Aggregation model root node. See Maven Mapping for details.
|
| Maven Result
|
true
false
|
false
|
Controls the output structure of the aggregated repo. If true, the aggregated repo will be Maven-conformant. Both the structure and meta-data of the aggregated repository will follow the conventions required by Maven.
NOTE that due to the flexibility of p2 (separation of meta-data about dependencies and location of artifacts) the aggregated repo will at the same time also function as a valid p2 repository.
|
| Packed Strategy
|
Copy
Verify
Unpack as Sibling
Unpack
Skip
|
Copy
|
This property controls how packed artifacts found in contributed repositories are handled when building the Aggregation:
- Copy - if the source contains packed artifacts, copy and store them verbatim. No further action
- Verify - same as copy but unpack the artifact and then discard the result
- Unpack as Sibling - same as copy but unpack the artifact and store the result as a sibling
- Unpack - use the packed artifact for data transfer but store it in unpacked form
- Skip - do not consider packed artifacts. This option will require unpacked artifacts in the source
|
| Sendmail
|
false
true
|
false
|
Controls whether or not emails are sent when errors are detected during the aggregation process. A value of false disables sending of emails (including mock emails).
|
| Type
|
S
I
N
M
C
R
|
S
|
Indicates the Aggregation type. This is an annotation merely for the benefit of the build master. It is not visible in the resulting repo.
- S - stable
- I - integration
- N - nightly
- M - milestone
- C - continuous
- R - release
|
Configuration
An Aggregation may have one or more Configuration definitions. The aggregated repo will be verified for all added configurations. If dependencies for any of the given configurations fails the aggregation as a whole fails. It is however possible to specify exceptions for individual Contributions.
A Configuration is a combination of the following properties:
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Architecture
|
X86
PPC
X86_64
IA64
IA64_32
Sparc
PPC64
S390
S390x
|
X86
|
Specifies the architecture for which this configuration should be verified.
|
| Enabled
|
true
false
|
true
|
Disables (false) or enables (true) the configuration for the aggregation process.
|
| Operating System
|
Win32
Linux
MacOSX
AIX
HPUX
Solaris
QNX
|
Win32
|
Specifies the operating system for which this configuration should be verified.
|
| Window System
|
Win32
GTK
Carbon
Cocoa
Motif
Photon
|
Win32
|
Specifies the windowing system for which this configuration should be verified.
|
Validation Set
The aggregator uses the p2 planner tool to determine what needs to be copied. The validation set determines the scope of one such planning session per valid configuration. This vouches for that everything that is contained within a validation set will be installable into the same target. Sometimes it is desirable to have more than one version of a feature in a repository even though multiple versions cannot be installed. This can be done using one validation set for each version.
A validation set can extend other validation set and thereby provide a convenient way for sharing common things that multiple validation sets will make use of. An extended validation set will not be validated by its own. It will only be validated as part of the sets that extend it.
A validation set can have two types of children: Contribution and Validation Repository.
Versions prior to 0.2.0 did not have the validation set node. Older aggr files will therefore be converted and given one validation set called main
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Description
|
<string>
|
-
|
An optional description of the validation set. For documentation purposes only.
|
| Enabled
|
true
false
|
true
|
Disables (false) or enables (true) the validation set to be considered in the aggregation process. Note that this may lead to missing dependencies and hence verification errors.
|
| Extends
|
<Validation Set>*
|
-
|
Zero or more references to Validation Sets defined in the given Aggregation model that this validation set extends.
|
| Label
|
<string>
|
-
|
Mandatory label for this validation set.
|
Contribution
Contributions are the key element of any aggregation. Contributions specify which repositories (or parts thereof (category, feature, product, IU)) to include, and the constraints controlling their inclusion in the aggregated repository.
A contribution definition may consist of several Mapped Repository and Maven Mapping components.
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Contacts
|
<Contact>*
|
-
|
Zero or more references to Contacts defined in the given Aggregation model. The referenced contacts will be notified if aggregation errors related to the contribution as a whole occur.
|
| Description
|
<string>
|
-
|
Optional description of the contribution. This is for documentation purposes only and will not end up in the aggregated repository.
|
| Enabled
|
true
false
|
true
|
Disables (false) or enables (true) the contribution to be considered in the aggregation process. Note that this may lead to missing dependencies and hence verification errors.
|
| Label
|
<string>
|
-
|
Mandatory label for this contribution.
|
| Maven Mappings
|
<Maven Mapping>*
|
-
|
See Maven Mapping for details ...
|
Mapped Repository
A Contribution may define several Mapped Repositories defining the actual content of the contribution. The Aggregator provides fine-grained control over the contribution from each Mapped Repository through references to Products, Bundles, Features, Categories, Exclusion Rules, Valid Configuration Rules.
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Category Prefix
|
<string>
|
-
|
A prefix added to the label of this repository when displayed in the p2 update manager. In the absence of custom categories this allows a useful grouping of repositories in an aggregated repository to be specified.
|
| Description
|
<string>
|
-
|
Description of the Mapped Repository. For documentation purposes only.
|
| Enabled
|
true
false
|
true
|
Controls whether a Mapped Repository is considered as part of the Contribution. Setting this property to false excludes the repository from the verification and aggregation process.
|
| Location
|
<URL>
|
|
This (required property) specifies the location of the repository that should be added to the enclosing Contribution.
|
| Mirror Artifacts
|
true
false
|
true
|
Controls whether the contents (artifacts) of the specified repository will be copied to the target location of the aggregated repository.
|
| Nature
|
<nature>
|
p2
|
This specifies the nature of the repository, i.e. which loader should be used for loading the repository. The number of available repository loaders depends on installed extensions. By default, p2 and maven2 loaders are present in the installation.
|
Product
Defining Product components allows the addition of individual Eclipse products to the aggregation to be specified (as opposed to mapping the complete contents of a given Mapped Repository. This naturally requires that products are present in the repositories being mapped.
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Description
|
<description>
|
-
|
Optional description of the mapping.
|
| Enabled
|
true
false
|
true
|
Controls whether a Product is considered as part of the Contribution. Setting this property to false excludes the product from the verification and aggregation process.
|
| Name
|
<product IU's id>
|
-
|
The id of the product to be included in the aggregation. A drop-down of available names is provided.
|
| Valid Configurations
|
<Configuration>*
|
-
|
References to zero or more configurations for which this product should be verified. If no references are given the product is verified for all Configurations defined for the aggregation.
|
| Version Range
|
<version range>
|
0.0.0
|
A version range that specifies acceptable versions for this installable unit. A pop-up editor is available.
|
Category
Defining Category components allows the addition of the content in specific categories (provided by the contributed repository) rather than the complete contents of a given Mapped Repository.
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Description
|
<description>
|
no value
|
Optional description of the mapping.
|
| Enabled
|
true
false
|
true
|
Controls whether a repository Category is considered as part of the Contribution. Setting this property to false excludes the category from the verification and aggregation process.
|
| Name
|
<category IU id>
|
-
|
The id of the category to be included in the aggregation. A drop-down of available names is provided.
|
| Label Override
|
<string>
|
-
|
New category name used instead of the default name.
|
| Valid Configurations
|
<Configuration>*
|
-
|
References to zero or more configurations for which the category contents should be verified. If no references are given the category is verified for all Configurations defined for the aggregation.
|
| Version Range
|
<version range>
|
0.0.0
|
A version range that specifies acceptable versions for this installable unit. A pop-up editor is available.
|
Bundle
Defining Bundle components allows addition of individual Eclipse bundles to the aggregation to be specified (rather than the complete contents of a given Mapped Repository).
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Description
|
<description>
|
no value
|
Optional description of the mapping.
|
| Enabled
|
true
false
|
true
|
Controls whether a referenced bundle is considered as part of the Contribution. Setting this property to false excludes the bundle from the verification and aggregation process.
|
| Name
|
<bundle IU id>
|
-
|
The id of the bundle to be included in the aggregation. A drop-down of available names is provided.
|
| Valid Configurations
|
<Configuration>*
|
-
|
References to zero or more configurations for which the referenced bundle has to be verified. If no references are given the bundle has to be verified for all Configurations defined for the aggregation.
|
| Version Range
|
<version range>
|
0.0.0
|
A version range that specifies acceptable versions for this installable unit. A pop-up editor is available.
|
Feature
Defining Feature components allows the addition of individual Eclipse features to the aggregation to be specified (rather than the complete contents of a given Mapped Repository). The features to include must be present in the mapped repository.
Furthermore, this component provides the means to group features implicitly into Custom Categories.
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Categories
|
<Custom Category>*
|
-
|
Optionally references the Custom Category definitions into which the feature should be placed upon aggregation. The relationship to the custom category is bi-directional so adding the feature to a custom category will update this property automatically in the Custom Category definition, and vice versa.
|
| Description
|
<description>
|
no value
|
Optional description of the mapping.
|
| Enabled
|
true
false
|
true
|
Controls whether a referenced feature is considered as part of the Contribution. Setting this property to false excludes the feature from the verification and aggregation process.
|
| Name
|
<feature IU id>
|
-
|
The id of the feature to be included in the aggregation. A drop-down of available names is provided.
|
| Valid Configurations
|
<Configuration>*
|
-
|
References to zero or more configurations for which the referenced feature should be verified. If no references are given the feature is verified for all Configurations defined for the aggregation.
|
| Version Range
|
<version range>
|
0.0.0
|
A version range that specifies acceptable versions for this installable unit. A pop-up editor is available.
|
Exclusion Rule
The Exclusion Rules provides an alternative way to control the content of the aggregated repository. An exclusion rule may specify exclusion of any bundle, feature or product. The excluded IU will not be considered in the aggregation and verification process. Each exclusion rule can only reference one IU id.
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Description
|
<string>
|
-
|
Description for documentation purposes.
|
| Name
|
<IU id>
|
-
|
The id of the installable unit to be excluded from the aggregation. A drop-down of available names is provided.
|
| Version Range
|
<version range>
|
0.0.0
|
A version range that specifies versions of this IU to be excluded. A pop-up editor is available.
|
Valid Configuration Rule
By default all contributed contents of a Mapped Repository will be verified for all Configurations defined for the aggregation. A Valid Configuration Rule provides more control over validation. When using a Valid Configuration Rule, the referenced IUs (product, feature, or bundle) will only be verified and aggregated for the configurations specified in the rule. The rule only applies if the whole repository is mapped (i.e. when no explicit features, products, bundles or categories are mapped, regardless if they are enabled or disabled).
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Description
|
<string>
|
-
|
Description for documentation purposes.
|
| Name
|
<IU id>
|
-
|
The id of the IU to be included in the verification process. A drop-down of available names is provided.
|
| Valid Configurations
|
<Configuration>*
|
-
|
References to one or more configurations for which the referenced IU should be verified. This implicitly excludes verification and aggregation for all other Configurations defined as part of the aggregation model.
|
| Version Range
|
<version range>
|
0.0.0
|
A version range that specifies versions of this installable unit for which the rule should apply. A pop-up editor is available.
|
Maven Mapping (Contribution)
See Maven Mapping for a detailed description and list of properties.
Contact
Defines a resuseable contact element which can be referenced in other parts of the model and may be used to send notifications about the aggregation process.
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Email
|
<email>
|
-
|
The email to be used when notifying the contact.
|
| Name
|
<string>
|
-
|
Full name of the contact. May be displayed as label when referenced in other parts of the model.
|
Custom Category
A Custom Category provides a grouping mechanism for features in the aggregated repository. A custom category can be referenced by Features defined for inclusion from a Mapped Repository.
The relationship to between Custom Category and a Feature is bi-directional. Thus, adding the feature to a custom category will update this property automatically in the Feature definition, and vice versa.
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Description
|
<string>
|
-
|
Description of the category as displayed when accessing the aggregated repository.
|
| Features
|
<Feature>*
|
-
|
Features included in this category by reference.
|
| Identifier
|
<string>
|
-
|
Category id. Required Eclipse category property.
|
| Label
|
<string>
|
-
|
Label displayed for the category when accessing the aggregated repository via the p2 update manager.
|
Validation Repository
A Validation Repository is used to define that a repository should be used when validating dependencies for the aggregation but whose contents should not be included in the aggregated repository.
It supports the cases where the objective is to create a repository that is not self sufficient, but rather a complement to something else (typical use case is an aggregation of everything produced by an organization with validation against the main Eclipse repository).
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Enabled
|
true
false
|
true
|
Controls whether a Validation Repository is considered during the verification and aggregation process. Setting this property to false excludes the repository from the verification and aggregation process.
|
| Location
|
<URL>
|
|
Specifies the location of the repository.
|
| Nature
|
<nature>
|
p2
|
This specifies the nature of the repository, i.e. which loader should be used for loading the repository. The number of available repository loaders depends on installed extensions. By default, p2 and maven2 loaders are present in the installation.
|
Maven Mapping
The Aggregator supports the creation of Maven-conformant repositories. A Maven repository requires a structure and use of naming conventions that may have to be achieved by a transformation of the Bundle-SymbolicName (BSN) when working with Eclipse bundles. There is a default translation from BSN naming standard to Maven naming. If that is not satisfactory,
custom transformations are supported by the definition of one or more Maven Mappings which can be defined at the Aggregator and the Contribution level.
This only applies when the Maven Result property of the Aggregator model is set to true. In that case all defined Maven Mappings are applied in the order in which they appear in the model starting from the most specific to the most generic. That means for each artifact that a Contribution adds to the aggregated repository:
- first Maven Mappings defined as children of a Contribution are applied in the order in which they appear as children of the parent Contribution node
- second Maven Mappings defined as children of the Aggregator model are applied in the order in which they appear as children of the parent Aggregator node
- finally the default Maven Mapping is applied
The most generic mapping is a default pattern that is applied whenever a Maven is created. It does not need to be added explicitly to the model.
A mapping is specified using a regular expression that is applied to each BSN. The regular expression must specify two replacements; one for the maven groupId, and one for the maven artifactId. The group and artifact ids have an effect on the resulting Maven repo structure. The default pattern is:
^([^.]+(?:\.[^.]+(?:\.[^.]+)?)?)(?:\.[^.]+)*$
The default maven mapping use the replacement $1 for groupId and $0 for artifactId. Hence, when applying the default maven mapping regular expression to a BSN, up to 3 segments (with dots as segment delimiters) are taken as the group id, and the entire BSN is taken as the artifact name. If this is a applied to something like org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.aggregator the groupId would be org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo and the artifactId org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.aggregator. The resulting Maven repo will have the folder structure:
org
|
eclipse
|
cbi
|
org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.aggregator
|
<folder name after version>
|
org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.aggregator-<version>.jar
...
| Property
|
Value(s)
|
Default Value
|
Comment
|
| Name Pattern
|
regex
|
-
|
A regular expression which is applied to the Bundle-SymbolicName (BSN). Pattern groups may be referenced in the replacement properties.
|
| Group Id
|
<string> (may contain pattern group references (i.e. $1, ...))
|
-
|
Group Id applied in a maven mapping structure (groupId/artifactId). The Group Id replacement may contain pattern group references (i.e. $1, ...).
|
| Artifact Id
|
<string> (may contain pattern group references (i.e. $1, ...))
|
-
|
Artifact Id applied in a maven mapping structure (groupId/artifactId). The Artifact Id replacement may contain pattern group references (i.e. $1, ...).
|
| Version Pattern
|
regex
|
-
|
An optional regular expression which is applied to the Version. Pattern groups may be referenced in the Version Template property.
|
| Version Template
|
<string> (may contain pattern group references (i.e. $1, ...))
|
-
|
If Version Pattern matched the given Version, then this Version Template is used to construct the version as seen in Maven, useful in particular to shorten versions ending in ".0" to 2-part versions etc.. The Version Template may contain pattern group references (i.e. $1, ...).
Since bug 406557 the special token "-SNAPSHOT" can be used after the main version part to denote a snapshot version.
If no Version Pattern is given or if the Version Pattern doesn't match, then the global strategy from Version Format is applied.
|
Legacy format support
[Note: this section is not completely accurate, with the current version of the CBI aggregator. It is certainly desired to offer this level of support, but that is not currently the case.]
As time passes, the aggregator model will undergo changes. All such changes will result in a new XML schema describing the aggregator model. The aggregator will always detect the schema in use by a model and, if needed, transform it into the current schema.
The transformation is fully automated when you run in headless mode but you will see a message like The build model file is obsolete, using the default transformation indicating that a transformation took place. The new model only exists in memory while the aggregation runs and is never stored on disk.
When you are opening an old model in the IDE, a transformation wizard will be presented where you are given a chance to specify a new file name for the transformed model. Please note that if you are using detached contributions (contributions that live in files of their own), and you want to keep it that way, then you should not change the name. If the name is changed, the aggregator has no choice but to create a new file that embeds all the contributions. This is because a detached contribution is referencing the aggregation file by name.
The behavior of the transformation wizard is:
- If the name is unchanged, also retain the detached contributions
- If a new name is given, embed all contributions in the new file
If you want a new name and still retain the detached contributions then you have two options
Either:
- Do the transformation using the same name
- Manually rename the main aggr file
- Manually search/replace and change the name in all your contributions
Or:
- Do the transformation using a different name
- Remove all your detached contributions
- Detach all contributions again
What else should be documented
- version editor (version formats...)
- how enable/disable on the context menu works
- drag&drop support
- 'available versions' tree
- context menu actions (mapping IUs from repository view, searching for IUs from 'available version' tree...)
Questions
- How is blame-mail handled when running in the UI? Are the options "production" etc. available then?
When launched from IDE, only --buildModel and --action options are set (all other options have default values). Perhaps it's worth adding a launching dialog which would enable setting all options that are available in headless mode.
- How do you know what the "log output url" is? How can it be set?
You can, for example, redirect a copy of the console output to a publicly available resource (a text file served by a http server). The public URL should be passed in the --logURL option so that a link to it would appear in the informational email.
- Some configurations seems to be missing - or is the list open ended? (Sparc, Motif, etc..) - I assume user can put anything there?
Only listed configurations are supported (they are a part of the model). Adding an option means changing the model and creation of a new aggregator build.
- It seems that it is possible to load maven repositories. I suppose the result of aggregation is a valid p2 repository (or a combination of p2/maven)??
Yes, it is possible to load p2 and maven2 repositories by default (if someone adds a custom loader then he can load any type of repository). The output is always p2 compatible, optionally combined with maven2 (with no extensibility - at least now). However, if a maven2 repo is loaded and the result is also maven2 compatible, it is not identical to the original (not all attributes loaded from maven are stored in the p2 model).
Information for developers of CBI aggregator
This section is to list "how to" information for developers (contributors and committers) of the code in the CBI Aggregator, not simply those using the CBI aggregator to combine p2 repositories.
Cloning the repo
The typical (Eclipse) methods apply:
git clone ssh://git.eclipse.org:29418/cbi/org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.aggregator
or
git clone ssh://<userid>@git.eclipse.org:29418/cbi/org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.aggregator
Building or Running locally
If desired, simply running mvn clean verify in the root of the repo will do a generic local build of the project. However, to do a clean build that is most like the production build, (after some possible edits for local customizing) one may take advantage of the script file named runLocalBuild.sh in
.../org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.releng.parent/localScripts
Similarly, in the same directory is a CBI Aggregator.launch file that will launch the CBI aggregator from Eclipse for running or debugging.
Production Build Jobs
The main build jobs for CBI aggregator are listed in a view at
https://ci.eclipse.org/cbi/view/p2RepoRelated/
This following list simply duplicates the documentation that describes the main jobs there and are listed in roughly the order they are typically ran in.
Job to run a build of CBI aggregator based on a Gerrit patch in master branch.
Job to run a build of CBI aggregator based on tip of master branch. This job is run manually when it is considered the right time to have a new "I-build" deployed to the two repository sites on the download server. Note: the "clean" in the name refers to only the "tmp" directory and the "local Maven Repository". If it is desired to literally wipe everything, then that should be done via the Jenkins "wipe workspace" function.
(Not always needed) this job is simply to remove some no longer needed repositories at the update sites for cbi.p2repo.aggregator.
This manual-only job creates the composites at .../cbi/updates/aggregator/ide/4.8 and .../cbi/updates/aggregator/headless/4.8.
We have a separate job for composites so that an I-build can be tested some before adding to the composite where everyone will get pseudo-automatically.
The composite XML files are literally re-created each time, based on the most recent three I-builds (so "bad" I-builds should be removed before running this job!).
This is a "script only" job, but the repository was left in source control, since technically the script here could be ran from its git version in
${WORKSPACE}/org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.aggregator/org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.releng.parent/buildScripts/writeComposites.sh
Standard XML Formatting
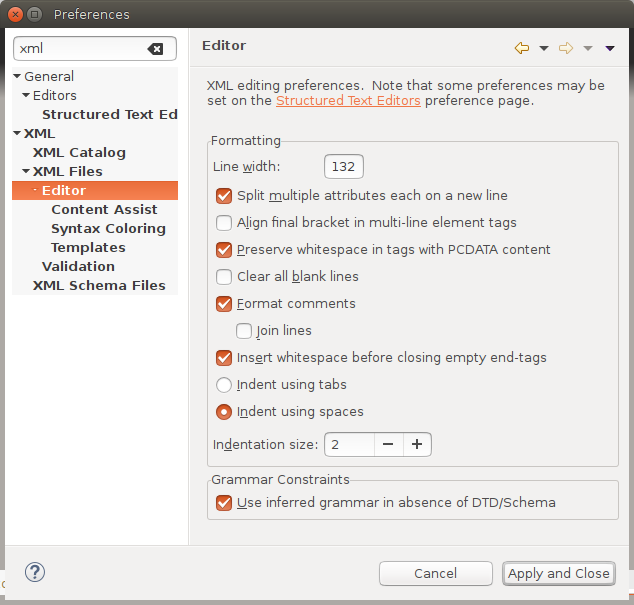
For this project, if a file that contains XML must be formatted, it must be formatted with the Eclipse XML Editor (this does NOT include EMF auto-created files!). So, first, naturally, the Eclipse XML Editor must be installed into your development environment.
Then, the default formatting preferences must be changed as follows:
- Line width: 132
- Split multiple attributes each on a new line (checked)
- Preserve whitespace in tags with PCDATA content: true (checked)
- Join lines: false (unchecked)
- Insert whitespace before closing empty end-tags: true (checked)
- Indent using spaces: true (checked)
- Indentation size: 2
Below is an image of what the XML Editor formatting preference page ends up looking.
Updating the .target file for this project
When to update
Typically the .target file is updated after every release to the Eclipse Platform since typically after every release of the Eclipse Platform there should be a new releasable build that is deployed and added to the composite update site. Occasionally, such as is there is major change to p2 during a development cycle, then the project needs to be branched with the maintenance branch being based purely on released prerequisites, with the master branch being based on the unreleased version of the Platform and its prerequisites.
How to update
Principles
Ultimately, the .target file should be treated as a ".txt" file so that the comments, spacing, and order of elements are not lost. (But there are ways around doing this literally, as described below).
Also, by convention -- for this project -- the repository location URLs are listed as specifically as possible.
Similarly, the versions of features and bundles are listed as specifically as possible.
Before committing changes, at a minimum be sure to go to preferences and select Target Platform and "Reload" and/or "Edit" to make sure that all URLs and versions are found. This is simply an easy way to spot typos, etc.
Manual Method
The manual method is the hardest way to update the .target file, but is often the safest way to be sure to get prerequisites which "match" the Eclipse Platform. When using the manual method, but .target file is edit with an ordinary text editor and typically copy/paste is used to update the required values (when needed -- not all prerequisites will need to be updated each time, but it is best to check each one to be sure).
The URLs are updated based on the specific URLs of the released prerequisites. For example, the Oxygen.3 release of the Eclipse Platform (4.7.3) has a download page that list both a general software site and a specific software site. For builds (and hence our .target file) we use the most specific URL available. (For updating our development installs, the general software site is typically fine).
To find out which versions are provided in that most recent site, one must simply go and look -- with by logging in with a shell account and navigating to the directory and then use something like ls -l to list the features or bundles of interest, and copy/paste the most recent version number to the .target file.
Or, one may also navigate to the web page of the software site and use the "Show Directory Contents" link to see features and bundles available along with their specific versions.
Tools Method
It is possible to use tools such as the Target Editor to simplify some of the editing, by using some pre- and post-steps that allows for comments to be maintained, etc. It also requires that the Eclipse XML Editor be installed and the formatting set to the project's Standard XML Formatting.
- First, copy the current (old) .target file in org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.releng.target to something like 'org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.aggregator.prereqs.target.save.xml'.
- Then open the .target file with the Target Editor, update the URLs as needed, then press the reload and update buttons as needed.
- Save that .target file, and notice the original formatting (and comments) are lost.
- Now rename or copy the .target file to something that ends with ".xml", for example, 'org.eclipse.cbi.p2repo.aggregator.prereqs.target.xml' and then format it with the XML Editor.
- Now that you have two xml files, one old, one new, you can do a "compare with each other" and should be a simple task to copy comments and formatting from one to the other.
- Once the comments and formatting has been restored, you can rename the ".xml file" back to simply the original ".target" file name.
Selecting the right bundle versions
The P2 URL for Orbit should point to the latest available release of the current branch, e.g. the Oxygen.3a Orbit release for the Oxygen branch. While the latest Orbit release should be used, the bundle versions of dependencies from Orbit should not necessarily be the latest version. Instead, the bundle versions of dependencies (e.g. SLF4J) should match the bundle versions that the Platform depends upon.
|